Relationship between transfusion burden, healthcare resource utilization, and complications in patients with beta-thalassemia in Taiwan: A real-world analysis
- PMID: 34505291
- PMCID: PMC9291481
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.16636
Relationship between transfusion burden, healthcare resource utilization, and complications in patients with beta-thalassemia in Taiwan: A real-world analysis
Abstract
Background: This study utilized a population-based claims database to identify patients with beta-thalassemia and evaluate associations between transfusion burden, healthcare resource utilization (HCRU), and complications.
Study design and methods: Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database was used to identify patients with beta-thalassemia (ICD-10 D56.1) in 2016. Patients with a beta-thalassemia claim in 2016 were indexed into the study at their first claim on or after January 1, 2001 in the dataset through to December 31, 2016 and followed until the end of study. During the follow-up period, red blood cell transfusion (RBCT) units, HCRU, iron chelation therapy use, and beta-thalassemia-related complications incidence were recorded. Patients were grouped into transfusion burden severity cohorts based on average number of RBCT units per 12 weeks during follow-up: 0 RBCT units, >0 to <6 RBCT units (mild), ≥6 to <12 RBCT units (moderate), and ≥12 RBCT units (severe).
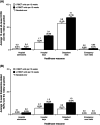
Results: A total of 2984 patients were included with mean follow-up of 6.95 years. Of these, 1616 (54.2%) patients had no claims for RBCT units, 1112 (37.3%) had claims for >0 to <6 RBCT units, 112 (3.8%) for ≥6 to <12 RBCT units, and 144 (4.8%) for ≥12 RBCT units per 12 weeks. Transfused patients had significantly more all-cause HCRU and iron chelation therapy compared with non-transfused patients during follow-up. Thalassemia-related HCRU and risk of liver, endocrine, cardiac, and renal complications were significantly and positively correlated with increases of RBCT units.
Discussion: Clinical and healthcare resource burden of patients with beta-thalassemia is closely related to transfusion burden.
Keywords: hemoglobinopathies; morbidity; outcomes; red blood cell transfusion.
© 2021 The Authors. Transfusion published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
Wesley Furnback, Bruce C.M. Wang, and Jackson Tang are paid consultants of Bristol Myers Squibb. Vicky W.‐H. Huang and Derek Tang are employees of Bristol Myers Squibb. Khaled M. Musallam received consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb. Chao‐Hsiun Tang and Meng‐Yao Lu have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Taher AT, Weatherall DJ, Cappellini MD. Thalassaemia. Lancet. 2018;391:155–67. - PubMed
-
- Cao A, Galanello R. Beta‐thalassemia. Genet Med. 2010;12:61–76. - PubMed
-
- Chern JPS, Lin KH, Su YN, Lu MY, Jou ST, Lin DT, et al. Impact of a national β‐thalassemia carrier screening program on the birth rate of thalassemia major. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2006;46:72–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical