Argon inhibits reactive oxygen species oxidative stress via the miR-21-mediated PDCD4/PTEN pathway to prevent myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 34506261
- PMCID: PMC8806883
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1965696
Argon inhibits reactive oxygen species oxidative stress via the miR-21-mediated PDCD4/PTEN pathway to prevent myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
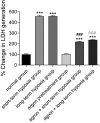
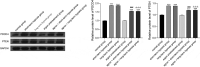
The objective of this study was to explore the effect of argon preconditioning on myocardial ischemia reperfusion (MI/R) injury and its mechanism. Cardiomyocytes H2C9 were pre-treated with 50% argon, and a cell model of oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) was established. CCK-8 and cytotoxicity detection kits were used to detect cell viability and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. The miR-21 expression was detected using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Western blot analysis was performed to detect the expression of programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) and homologous phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) proteins. The levels of inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8) and oxidative stress factors (reactive oxygen species ROS], malondialdehyde [MDA], and superoxide dismutase [SOD]) were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The effect of argon on cell apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry. Argon increased the proliferation of cardiomyocytes induced by OGD, decreased the release of LDH in cell culture medium, increased miR-21 expression in cells, decreased the expression of miR-21 target proteins PDCD4 and PTEN, decreased the levels of inflammatory factors (interleukin-1β [IL-1β], interleukin-6 [IL-6], and interleukin-8 [IL-8]) and oxidative stress factors (ROS and MDA), increased the SOD content, and decreased the cell apoptosis rate. Our results suggest that argon preconditioning inhibited the PDCD4/PTEN pathway via miR-21, thereby inhibiting ROS oxidative stress and preventing MI/R injury.
Keywords: Argon; PDCD4/PTEN pathway; ROS oxidative; miR-21.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Heusch G, Gersh BJ.. The pathophysiology of acute myocardial infarction and strategies of protection beyond reperfusion: a continual challenge. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:774–784. - PubMed
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM.. Targeting myocardial reperfusion injury–the search continues. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(11):1073–1075. - PubMed
-
- Qi H, Soto-Gonzalez L, Krychtiuk KA, et al. Pretreatment with argon protects human cardiac myocyte-like progenitor cells from oxygen glucose deprivation-induced cell death by activation of AKT and differential regulation of mapkinases. Shock. 2018;49(5):556–563. . - PubMed
-
- Kiss A, Shu H, Hamza O, et al. Argon preconditioning enhances postischaemic cardiac functional recovery following cardioplegic arrest and global cold ischaemia. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;54(3):539–546. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
