Biomarker Evidence of the Persistent Inflammation, Immunosuppression and Catabolism Syndrome (PICS) in Chronic Critical Illness (CCI) After Surgical Sepsis
- PMID: 34506322
- PMCID: PMC8592255
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005067
Biomarker Evidence of the Persistent Inflammation, Immunosuppression and Catabolism Syndrome (PICS) in Chronic Critical Illness (CCI) After Surgical Sepsis
Abstract
Objective: To analyze serial biomarkers of the persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome (PICS) to gain insight into the pathobiology of chronic critical illness (CCI) after surgical sepsis.
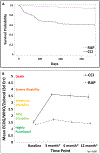
Background: Although early deaths after surgical intensive care unit sepsis have decreased and most survivors rapidly recover (RAP), one third develop the adverse clinical trajectory of CCI. However, the underlying pathobiology of its dismal long-term outcomes remains unclear.
Methods: PICS biomarkers over 14 days from 124 CCI and 225 RAP sepsis survivors were analyzed to determine associations and prediction models for (1) CCI (≥14 intensive care unit days with organ dysfunction) and (2) dismal 1-year outcomes (Zubrod 4/5 performance scores). Clinical prediction models were created using PIRO variables (predisposition, insult, response, and organ dysfunction). Biomarkers were then added to determine if they strengthened predictions.
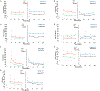
Results: CCI (vs RAP) and Zubrod 4/5 (vs Zubrod 0-3) cohorts had greater elevations in biomarkers of inflammation (interleukin [IL]-6, IL-8, interferon gamma-induced protein [IP-10], monocyte chemoattractant protein 1), immunosuppression (IL-10, soluble programmed death ligand-1), stress metabolism (C-reactive protein, glucagon-like peptide 1), and angiogenesis (angiopoietin-2, vascular endothelial growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1, stromal cell-derived factor) at most time-points. Clinical models predicted CCI on day 4 (area under the receiver operating characteristics curve [AUC] = 0.89) and 1 year Zubrod 4/5 on day 7 (AUC = 0.80). IL-10 and IP-10 on day 4 minimally improved prediction of CCI (AUC = 0.90). However, IL-10, IL-6, IL-8, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, IP-10, angiopoietin-2, glucagon-like peptide 1, soluble programmed death ligand-1, and stromal cell-derived factor on day 7 considerably improved the prediction of Zubrod 4/5 status (AUC = 0.88).
Conclusions: Persistent elevations of PICS biomarkers in the CCI and Zubrod 4/5 cohorts and their improved prediction of Zubrod 4/5 validate that PICS plays a role in CCI pathobiology.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
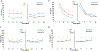


References
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. - PubMed
-
- Moore LJ, McKinley BA, Turner KL, et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in general surgery patients. J Trauma. 2011;70:672–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

