Prevalence of Hypertension in a Community
- PMID: 34506387
- PMCID: PMC8028540
- DOI: 10.31729/jnma.5316
Prevalence of Hypertension in a Community
Abstract
Introduction: Hypertension is one of the leading risk factors for the global burden of disease and is of rising public health concerns in the developing world including Nepal. However, few studies have focused on awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among people living with this condition. In this scenario, this study aimed to find out the prevalence of hypertension and its awareness, treatment, and control among hypertensive patients residing in different parts of Kaski district, Nepal.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was performed among 977 family members of 290 households from August to December 2017. Ethical approval was taken from the Institutional Review Committee (reference number:73/074/75) of the Pokhara University Research Center. Simple random sampling was done. Hypertension screening was performed through averaging three values obtained by standardized aneroid sphygmomanometer in three observations. Primary data was collected through self-administered questionnaires and face-to-face interviews based on the participant's preferences. Collected data were analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 20. Point estimate at 95% Confidence Interval was calculated along with frequency and proportion for binary data.
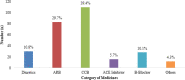
Results: Out Of total 997 family members screened, 294 (29.49%) (26.66-32.32 at 95% confidence interval) had hypertension whereas only 127 (43.2%) were completely aware of their disease condition. 279 (94.9%) were taking antihypertensive medication and 201 (68.4%) had their blood pressure controlled.
Conclusions: We found that almost one-fourth of the adult population in the community suffered from hypertension but less than half of the hypertensive patients are aware of their conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. Acomparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2224–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO . Key facts: World Health Organization [Internet] Geneva: WHO; 2019. [2020 Oct 17;]. Hypertension.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension Available from:
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical