Potential of herbal products in prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Literature review
- PMID: 34507112
- PMCID: PMC8410512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112150
Potential of herbal products in prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Literature review
Abstract
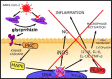
The COVID-19 epidemic is the greatest pandemic that human kind experienced for decades, with high morbidity and mortality. Despite recent development of vaccines there is still many severe cases of COVID-19. Unfortunately there is still no standardized therapies and treatment of severe cases is very challenging. The aim of this study is to indicate if herbs administered alone or as a complementary therapy could be used as prophylaxis or treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Over 85% of patients with COVID-19 in China used Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and a most common herb is Glycyrrhiza glabra, which in vitro inhibits replication of different enveloped viruses, including coronaviruses. Glycyrrhizin in vitro connects and changes conformation of ACE2 receptors, which are vital for SARS-CoV-2 penetration into host cells. Pelargonium sidoides show immunomodulatory and antiviral properties in clinical and in vitro studies, and it inhibits replication of HCo-229E coronavirus. Glycyrrhiza glabra in combination with standard therapies significantly reduces the hospitalization rate and occurrence of COVID-19 symptoms. As complementary therapies lianhuaqingwen capsules and jinhua qinggan granules reduces hospitalization rates, time to symptoms recovery and improve patient psychological comfort. In view of SARS-CoV-2 other herbs are not effective, e.g. maxingshigan-yinqiaosan, or therapeutic concentration would be impossible to achieve, e.g. ephedra herb, or there is simply no proper data. Therefore, Liquorice and Pelargonium sidoides are effective against coronaviruses and could be possibly used as prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, while lianhuaqingwen capsules and jinhua qinggan granules can be useful as a complementary therapy to conventional treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Glycyrrhiza glabra; Glycyrrhizin; Pelargonium sidoides; Traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potential Role of Gut Microbiota in Traditional Chinese Medicine against COVID-19.Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(4):785-803. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X21500373. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Am J Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 33853498 Review.
-
Traditional Chinese herbal medicine at the forefront battle against COVID-19: Clinical experience and scientific basis.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jan;80:153337. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153337. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33221457 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine to treat COVID-19: the importance of evidence-based research.Drug Discov Ther. 2020;14(3):149-150. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2020.03054. Drug Discov Ther. 2020. PMID: 32669523
-
The direct evidence and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of COVID-19.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111267. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111267. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33508618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine as the Preventive and Therapeutic Remedy for COVID-19.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(21):3118-3131. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230331084126. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 36999715 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology to Reveal the Mechanisms of Forsythia suspensa Extract Against Respiratory Syncytial Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 29;26(11):5244. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115244. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508053 Free PMC article.
-
An exhaustive comprehension of the role of herbal medicines in Pre- and Post-COVID manifestations.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 5;296:115420. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115420. Epub 2022 May 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35654349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico evidence implicating novel mechanisms of Prunella vulgaris L. as a potential botanical drug against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 18;14:1188086. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1188086. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37274117 Free PMC article.
-
Tongue and pulse features of 668 asymptomatic patients infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 omicron variant in Shanghai.J Tradit Chin Med. 2022 Dec;42(6):1006-1011. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220922.004. J Tradit Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36378060 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying in-market application of Pelargonium root extract EPs 7630 for the treatment of COVID-19: analysis of pharmacovigilance data.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 23;15:1335309. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1335309. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38464728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard, 21 June, 2021. 〈https://covid19.who.int/〉.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

