Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 6 regulated by miR-27a-3p attenuates tumor proliferation in breast cancer
- PMID: 34510318
- PMCID: PMC8885522
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-021-02704-8
Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 6 regulated by miR-27a-3p attenuates tumor proliferation in breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a bioactive molecule which participates in many physical and pathological processes. Although LPA receptor 6 (LPAR6), the last identified LPA receptor, has been reported to have diverse effects in multiple cancers, including breast cancer, its effects and functioning mechanisms are not fully known.
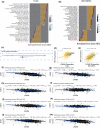
Methods: Multiple public databases were used to investigate the mRNA expression of LPAR6, its prognostic value, and potential mechanisms in breast cancer. Western blotting was performed to validate the differential expression of LPAR6 in breast cancer tissues and their adjacent tissues. Furthermore, in vitro experiments were used to explore the effects of LPAR6 on breast cancer. Additionally, TargetScan and miRWalk were used to identify potential upstream regulating miRNAs and validated the relationship between miR-27a-3p and LPAR6 via real-time polymerase chain reaction and an in vitro rescue assay.
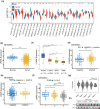
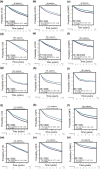
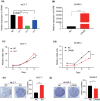
Results: LPAR6 was significantly downregulated in breast cancer at transcriptional and translational levels. Decreased LPAR6 expression in breast cancer is significantly correlated with poor overall survival, disease-free survival, and distal metastasis-free survival, particularly for hormone receptor-positive patients, regardless of lymph node metastatic status. In vitro gain and loss-of-function assays indicated that LPAR6 attenuated breast cancer cell proliferation. The analyses of TCGA and METABRIC datasets revealed that LPAR6 may regulate the cell cycle signal pathway. Furthermore, the expression of LPAR6 could be positively regulated by miR-27a-3p. The knockdown of miR-27a-3p increased cell proliferation, and ectopic expression of LPAR6 could partly rescue this phenotype.
Conclusion: LPAR6 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer and is positively regulated by miR-27a-3p.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cell proliferation; Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 6; miR-27a-3p.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 6 (LPAR6) Expression and Prospective Signaling Pathway Analysis in Breast Cancer.Mol Diagn Ther. 2019 Feb;23(1):127-138. doi: 10.1007/s40291-019-00384-3. Mol Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 30694446
-
Inverse correlation of miR-27a-3p and CDH5 expression serves as a diagnostic biomarker of proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Apr;220:153393. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153393. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33740544
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced exosomal miR-27a-3p promotes immune escape in breast cancer via regulating PD-L1 expression in macrophages.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(17):9560-9573. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15367. Epub 2020 Jul 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32672418 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-27a-3p enhances the cisplatin sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt pathway.Biosci Rep. 2021 Dec 22;41(12):BSR20192007. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192007. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34096570 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27a-3p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor and Regulates Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation via Targeting HOXB8.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan 1;18:1533033819861971. doi: 10.1177/1533033819861971. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. Retraction in: Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211039605. doi: 10.1177/15330338211039605. PMID: 31319766 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Potential Impact of PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway Genes, KLF-14, MDM4, miRNAs 27a, miRNA-196a Genetic Alterations in the Predisposition and Progression of Breast Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;15(4):1281. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041281. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831624 Free PMC article.
-
Nerves in gastrointestinal cancer: from mechanism to modulations.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Dec;19(12):768-784. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00669-9. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36056202 Review.
-
Prognostic analysis of E2F transcription factors E2F1 and E2F3 in four independent pediatric neuroblastoma cohorts.BMC Pediatr. 2022 Jun 29;22(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12887-022-03424-w. BMC Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35764946 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Ionizing Irradiation on the Autotaxin-Lysophasphatidic Acid Axis and Interleukin-6/8 Secretion in Different Breast Cancer Cell Lines.J Pers Med. 2024 Sep 12;14(9):968. doi: 10.3390/jpm14090968. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39338222 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of LPAR6 and CAB39L dysregulates the basal-to-luminal urothelial differentiation program, contributing to bladder carcinogenesis.Cell Rep. 2024 May 28;43(5):114146. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114146. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38676926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):33. - PubMed
-
- Liang Y, Zhang H, Song X, Yang Q. Metastatic heterogeneity of breast cancer: molecular mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Seminars Cancer Biol. 2020;60:14–27. - PubMed
-
- Ueda H. Pathogenic mechanisms of lipid mediator lysophosphatidic acid in chronic pain. Prog Lipid Res. 2020;81:101079. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

