Surgical management of spinal tuberculosis with a two-stage posterior instrumentation with bridging: a case report
- PMID: 34512950
- PMCID: PMC8427878
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjab406
Surgical management of spinal tuberculosis with a two-stage posterior instrumentation with bridging: a case report
Abstract
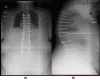
Tuberculosis (TB) affects millions of people every year. Spinal TB is a common extrapulmonary manifestation of the disease. Spinal TB can be devastating and carries an unfortunate outcome. Herein, we present an atypical spinal TB that was treated initially based on intraoperative cultures with posterior decompression and instrumentation of T11-L3 with directed antibiotic therapy. Recurrence of the lesion and failure of instrumentation necessitated further investigation and intervention 1 year later. Using a two-stage surgical procedure leaving the infected spine to heal first with directed anti-TB medications. The patient was managed using posterior instrumentation with bridging from T5 to the pelvis, spanning the destructed area and utilizing a bridging technique with multiple rod constructs across the infected spine. Here, we present the benefit of using the bridging technique to promote bone healing and achieve a solid fixation.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. © The Author(s) 2021.
Figures
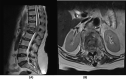

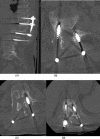
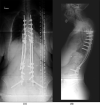
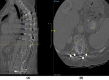

References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2020, Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
-
- Glaziou P, Floyd K, Raviglione MC. Global epidemiology of tuberculosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2018;39:271–85. - PubMed
-
- Alateah SM, Othman MW, Ahmed M, Al Amro MS, Al Sherbini N, Ajlan HH. A retrospective study of tuberculosis prevalence amongst patients attending a tertiary hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis 2020;21:100185.Published 2020 Sep 22. 10.1016/j.jctube.2020.1001855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

