Micro/nanotechnology-inspired rapid diagnosis of respiratory infectious diseases
- PMID: 34513114
- PMCID: PMC8424173
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-021-00206-8
Micro/nanotechnology-inspired rapid diagnosis of respiratory infectious diseases
Abstract
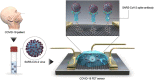
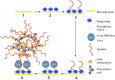
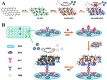
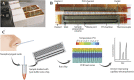
Humans have suffered from a variety of infectious diseases since a long time ago, and now a new infectious disease called COVID-19 is prevalent worldwide. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has led to research of the effective methods of diagnosing respiratory infectious diseases, which are important to reduce infection rate and help the spread of diseases be controlled. The onset of COVID-19 has led to the further development of existing diagnostic methods such as polymerase chain reaction, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Furthermore, this has contributed to the further development of micro/nanotechnology-based diagnostic methods, which have advantages of high-throughput testing, effectiveness in terms of cost and space, and portability compared to conventional diagnosis methods. Micro/nanotechnology-based diagnostic methods can be largely classified into (1) nanomaterials-based, (2) micromaterials-based, and (3) micro/nanodevice-based. This review paper describes how micro/nanotechnologies have been exploited to diagnose respiratory infectious diseases in each section. The research and development of micro/nanotechnology-based diagnostics should be further explored and advanced as new infectious diseases continue to emerge. Only a handful of micro/nanotechnology-based diagnostic methods has been commercialized so far and there still are opportunities to explore.
Keywords: Micro/nanodevices; Micro/nanotechnology-based diagnostic methods; Micromaterials; Nanomaterials; Respiratory infectious diseases.
© Korean Society of Medical and Biological Engineering 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures













Similar articles
-
Nanotechnology: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(19):1-43. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074489 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): A Rapid, Sensitive, Specific, and Cost-Effective Point-of-Care Test for Coronaviruses in the Context of COVID-19 Pandemic.Biology (Basel). 2020 Jul 22;9(8):182. doi: 10.3390/biology9080182. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32707972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of molecular biology and nanotechnology based analytical methods for the detection of SARS-CoV-2: promising biotools for the rapid diagnosis of COVID-19.Analyst. 2021 Mar 7;146(5):1489-1513. doi: 10.1039/d0an01528h. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Analyst. 2021. PMID: 33543178
-
Engineered two-dimensional nanomaterials based diagnostics integrated with internet of medical things (IoMT) for COVID-19.Chem Soc Rev. 2024 Apr 22;53(8):3774-3828. doi: 10.1039/d3cs00719g. Chem Soc Rev. 2024. PMID: 38433614 Review.
-
Multiplex reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Oct 15;166:112437. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112437. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32692666 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles in Biomedical Sciences: Properties, Current Trends, Novel Opportunities and Emerging Challenges in Theranostic Nanomedicine.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;13(3):424. doi: 10.3390/nano13030424. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36770385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polysaccharide-Based Nanomedicines Targeting Lung Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 13;14(12):2788. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122788. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multitask Siamese Network for Remote Photoplethysmography and Respiration Estimation.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;22(14):5101. doi: 10.3390/s22145101. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890781 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging strategies in nanotechnology to treat respiratory tract infections: realizing current trends for future clinical perspectives.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2442-2458. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2089294. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35892224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beveridge WIB. The chronicle of influenza epidemics. Hist Philos Life Sci. 1991;13(2):223–234. - PubMed
-
- Raoult D, Drancourt M. Paleomicrobiology: past human infections; 2008.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
