Automated microscope-independent fluorescence-guided micropipette
- PMID: 34513218
- PMCID: PMC8407805
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.431372
Automated microscope-independent fluorescence-guided micropipette
Abstract
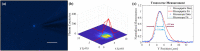
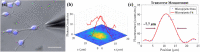
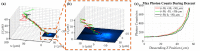
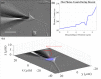
Glass micropipette electrodes are commonly used to provide high resolution recordings of neurons. Although it is the gold standard for single cell recordings, it is highly dependent on the skill of the electrophysiologist. Here, we demonstrate a method of guiding micropipette electrodes to neurons by collecting fluorescence at the aperture, using an intra-electrode tapered optical fiber. The use of a tapered fiber for excitation and collection of fluorescence at the micropipette tip couples the feedback mechanism directly to the distance between the target and electrode. In this study, intra-electrode tapered optical fibers provide a targeted robotic approach to labeled neurons that is independent of microscopy.
© 2021 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vélez-Fort M., Rousseau C. V., Niedworok C. J., Wickersham I. R., Rancz E. A., Brown A. P., Strom M., Margrie T. W., “The stimulus selectivity and connectivity of layer six principal cells reveals cortical microcircuits underlying visual processing,” Neuron 83(6), 1431–1443 (2014).10.1016/j.neuron.2014.08.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holst G. L., Stoy W., Yang B., Kolb I., Kodandaramaiah S. B., Li L., Knoblich U., Zeng H., Haider B., Boyden E. S., Forest C. R., “Autonomous patch-clamp robot for functional characterization of neurons in vivo: development and application to mouse visual cortex,” J. Neurophysiol. 121(6), 2341–2357 (2019).10.1152/jn.00738.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
