Roles of microRNAs in tumorigenesis and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34513596
- PMCID: PMC8394161
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i8.609
Roles of microRNAs in tumorigenesis and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the major subtype of esophageal cancer that is prevalent in Eastern Asia. Despite recent advances in therapy, the outcome of ESCC patients is still dismal. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding RNAs which can negatively modulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. The involvement and roles of miRNAs have become one of the hot topics of cancer research in recent years. In ESCC, genetic variations within miRNA coding genes were found to have distinct epidemiological significance in different populations. Dysregulated expression of several miRNAs was reported to be associated with therapeutic response. Functionally, miRNAs can act either in an oncogenic or a tumor-suppressive manner during tumorigenesis of ESCC by interrupting signaling pathways associated with cell proliferation, metabolism, cancer stemness, and resistance to chemo- or radiotherapy. Moreover, miRNAs modulate metastasis of ESCC by targeting genes that regulate cytoskeleton dynamics, extracellular matrix remodeling, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and tumor microenvironment. Most importantly, mounting evidence suggests that inhibiting oncogenic miRNAs or restoring the loss of tumor-suppressive miRNAs has therapeutic potential in the treatment of ESCC. Here, we review and discuss recent studies on the significance, biological functions, and therapeutic potential of miRNAs in tumorigenesis and metastasis of ESCC.
Keywords: Dysregulation; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Metastasis; MicroRNAs; Therapeutic potential; Tumorigenesis.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
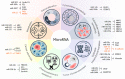
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381:400–412. - PubMed
-
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–2252. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut. 2015;64:381–387. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

