Ultra-brief crisis interpersonal psychotherapy based intervention for suicidal children and adolescents
- PMID: 34513604
- PMCID: PMC8394689
- DOI: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i8.403
Ultra-brief crisis interpersonal psychotherapy based intervention for suicidal children and adolescents
Abstract
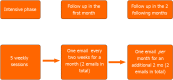
Suicidal behaviors in adolescence are a major public health concern. The dramatic rise in self-injurious behaviors among adolescents has led to an overwhelming increase in the number of those presenting to the emergency rooms. The intervention described below was constructed on the basis of brief and focused interventions that were found to be effective among suicidal adults using an adaptation of interpersonal psychotherapy for adolescents. The intervention has four main objectives: first, a focused treatment for reducing suicide risk; second, a short and immediate response; third, building a treatment plan based on understanding the emotional distress and interpersonal aspects underlying suicidal behavior; and lastly, to generate hope among adolescents and their parents. The intervention includes intensive five weekly sessions, followed by 3 mo of email follow-up.
Keywords: Adolescents; Crisis intervention; Depression; Interpersonal psychotherapy; Suicide.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Haruvi Catalan L, Levis Frenk M, Adini Spigelman E, Engelberg Y, Barzilay S, Mufson L, Apter A, Benaroya Milshtein N, Fennig S, Klomek AB. Ultra-Brief Crisis IPT-A Based Intervention for Suicidal Children and Adolescents (IPT-A-SCI) Pilot Study Results. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:553422. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hill RM, Rufino K, Kurian S, Saxena J, Saxena K, Williams L. Suicide Ideation and Attempts in a Pediatric Emergency Department Before and During COVID-19. Pediatrics . 2021;147:e2020029280. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources