Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
- PMID: 34513639
- PMCID: PMC8410998
- DOI: 10.5395/rde.2021.46.e33
Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of ionic and non-ionic-based contrast media (in vitro study) and the combinatorial effect of chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution (CERS) (in vivo study) for visualization of the root canal anatomy.
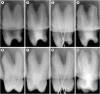
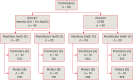
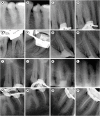
Materials and methods: In vitro study (120 teeth): The root canal of maxillary premolars and molars (in vitro group 1 and 2 respectively, n = 60 each) were analyzed using 4 different contrast media (subgroups: Omnipaque 350, Iopamidol, Xenetix 350, and Urografin 76; n = 15 each) in combination with 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Based on the results of the in vitro study, in vivo study (80 teeth) was done to compare Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl with CERS (in vivo group 1 and 2 respectively, n = 40 each) on maxillary and mandibular premolars and molars. Two endodontists used radiovisiography to assess the depth of ingress and identify the aberrant root anatomy after access cavity preparation, and after initial cleaning and shaping of canals. Kruskal-Wallis test was used for in vitro comparison (p < 0.05), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Mann-Whitney U test for in vivo analysis (p < 0.01).
Results: In vitro study, Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl facilitated a significant higher visualization (p < 0.05). For in vivo study, CERS had a statistically significant depth of ingress (p < 0.01), and was efficient in identifying the aberrant root canal anatomy of premolars and molars.
Conclusions: CERS facilitates better visualization of the root canal anatomy of human premolars and molars.
Keywords: Chitosan; Contrast media; Digital radiography; Root canal anatomy.
Copyright © 2021. The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Vertucci FJ. Root canal morphology and its relationship to endodontic procedures. Endod Topics. 2005;10:3–29.
-
- Cleghorn BM, Christie WH, Dong CC. The root and root canal morphology of the human mandibular first premolar: a literature review. J Endod. 2007;33:509–516. - PubMed
-
- Sachdeva GS, Ballal S, Gopikrishna V, Kandaswamy D. Endodontic management of a mandibular second premolar with four roots and four root canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case report. J Endod. 2008;34:104–107. - PubMed
-
- Barker BC, Parsons KC, Mills PR, Williams GL. Anatomy of root canals. I. Permanent incisors, canines and premolars. Aust Dent J. 1973;18:320–327. - PubMed
-
- Hession RW. Endodontic morphology. I. An alternative method of study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1977;44:456–462. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

