EUS in Pediatrics: A Multicenter Experience and Review
- PMID: 34513763
- PMCID: PMC8424044
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.709461
EUS in Pediatrics: A Multicenter Experience and Review
Abstract
Background/Aim: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a well-established tool used in the evaluation and treatment of a wide range of pathologies in adult medicine. EUS in pediatrics has been shown to be safe and technically effective, and its use continues to evolve. This article aims to describe the EUS experience at our tertiary-care centers with regard to safety, technical success, and its impact in clinical management. We also discuss the current and developing diagnostic and therapeutic uses for EUS in pediatrics such as in pancreaticobiliary disease, congenital anomalies, eosinophilic esophagitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and liver disease. Methods: This is a retrospective review of EUS performed by two pediatric gastroenterologists trained as endosonographers between April 2017 and November 2020. Patient demographics, procedure indication, procedure characteristics, technical success, and complications were collected. Literature review was performed to describe current and future uses of EUS in pediatrics. Results: Ninety-eight EUS were performed with 15 (15.3%) including fine needle aspiration/biopsy and 9 (9.2%) cases being therapeutic. Most common indications include choledocholithiasis (n = 31, 31.6%), pancreatic fluid collections (n = 18, 18.4%), chronic and acute recurrent pancreatitis (n = 14, 14.3%), and acute pancreatitis characterization (n = 13, 13.3%). Notable indications of pancreatic mass (n = 6, 6.1%) and luminal lesions/strictures (n = 6, 6.1%) were less common. Complications were limited with one instance of questionable GI bleeding after cystgastrostomy creation. Ninety-eight of 98 (100%) cases were technically successful. Conclusion/Discussion: EUS has been shown to be performed safely and successfully in the pediatric population by pediatric endosonographers. This study and review support its use in pediatric practice and demonstrate the wide variety of indications for EUS such as pancreatic cystgastrostomy, celiac plexus neurolysis, and evaluation of chronic pancreatitis. This literature review also demonstrates areas of potential development for EUS within the practice of pediatric gastroenterology.
Keywords: endoscopic ultrasonography; pancreatic fluid collection; pancreatitis; pediatric; pediatric gastroenterologists.
Copyright © 2021 Piester and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
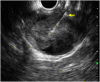
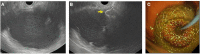
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

