Women in International Elite Athletics: Gender (in)equality and National Participation
- PMID: 34514387
- PMCID: PMC8429847
- DOI: 10.3389/fspor.2021.709640
Women in International Elite Athletics: Gender (in)equality and National Participation
Abstract
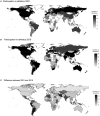
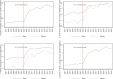
Gender discrimination has been strongly related to the suppression of women's participation in sport. Accordingly, gender (in)equality has proven to be an important determinant for the participation and the success of countries in international women's elite sport. Hence, differences in gender (in)equalitity, such as women's participation in the labor force, fertility rates, tradition of women suffrage or socio-economic status of women, could be linked to success in international women's elite sports. While major international sport governing bodies have created programs to subsidize the development of women's sports in member countries, gender equality has figured rather low within the International Amateur Athletics Federation (IAAF) (now World Athletics). Therefore, the paper examines the impact of gender (in)equality on country participation in international athletics on the base of a unique dataset on season's bests. The results provide further support that gender inequality matters and is associated with participation in women's elite sports. Whereas, women's participation in athletics has made considerable progress in the past two decades as a side-effect of the IAAF's decentralization strategy, the analyses illustrate the need for better targeted and better resourced development programs for increasing participation of less gender equal countries. Moreover, the analyses indicate the limitations of a pure macro-social approach as there are some rather unexpected dynamic developments, such as, the substantial progress of women's athletics in the Islamic Republic of Iran as a country with strong Muslim religious affiliation. The results from this analysis were used to provide practical implications.
Keywords: development programs; gender inequality; international athletics; multi-level analyses; women's empowerment.
Copyright © 2021 Meier, Konjer and Krieger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Anthonj P., Emrich E., Flatau J., Hämmerle M., Rohkohl F. (2013). The Development of Women's Athletics-Findings of an Empirical Analysis. Saarbrücken: Universaar.
-
- Bechthold I. (2002a). Fax, 11 September 2002, collection “Ilse Bechthold”. Münster: University of Münster.
-
- Bechthold I. (2002b). Letter to Lamine Diack, 1 May 2002, collection “Ilse Bechthold”. Münster: University of Münster.
-
- Bernard A. B., Busse M. R. (2004). Who wins the olympic games: economic resources and medal totals. Rev. Econ. Statist. 86, 413–417. 10.1162/003465304774201824 - DOI
-
- Brighton Declaration on Women and Sport (1994). Brighton Declaration on Women and Sport. Brighton: Sports Council.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

