A data-driven architecture using natural language processing to improve phenotyping efficiency and accelerate genetic diagnoses of rare disorders
- PMID: 34514437
- PMCID: PMC8432593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2021.100035
A data-driven architecture using natural language processing to improve phenotyping efficiency and accelerate genetic diagnoses of rare disorders
Abstract
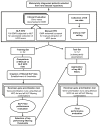
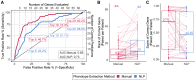
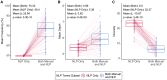
Effective genetic diagnosis requires the correlation of genetic variant data with detailed phenotypic information. However, manual encoding of clinical data into machine-readable forms is laborious and subject to observer bias. Natural language processing (NLP) of electronic health records has great potential to enhance reproducibility at scale but suffers from idiosyncrasies in physician notes and other medical records. We developed methods to optimize NLP outputs for automated diagnosis. We filtered NLP-extracted Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) terms to more closely resemble manually extracted terms and identified filter parameters across a three-dimensional space for optimal gene prioritization. We then developed a tiered pipeline that reduces manual effort by prioritizing smaller subsets of genes to consider for genetic diagnosis. Our filtering pipeline enabled NLP-based extraction of HPO terms to serve as a sufficient replacement for manual extraction in 92% of prospectively evaluated cases. In 75% of cases, the correct causal gene was ranked higher with our applied filters than without any filters. We describe a framework that can maximize the utility of NLP-based phenotype extraction for gene prioritization and diagnosis. The framework is implemented within a cloud-based modular architecture that can be deployed across health and research institutions.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.R.P. is the owner and founder of J Square Labs LLC. J.R.P, T.D., P.M., J.R., and S.L. are current or former employees or consultants of Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and C.Y., R.G., T.W., M.M., A.B., and A.F. are current or former employees of Clinithink Ltd. J.R.P. has consulted for and received compensation from GNS Health-care and TCB Analytics. J.R. is the owner and founder of Latent Strategies, LLC. A.H.B. has received funding from the NIH, MDA (USA), AFM Telethon, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Audentes Therapeutics Inc., Dynacure SAS, and Pfizer Inc. He has consulted and received compensation or honoraria from Asklepios BioPharmaceutical, Inc., Audentes Therapeutics, Biogen, F. Hoffman-La Roche AG, GLG, Inc., Guidepoint Global, and Kate Therapeutics and holds equity in Ballard Biologics and Kate Therapeutics. P.B.A. is on the Clinical Advisory Board of Illumina Inc. and GeneDx. C.A.B. has consulted for, and received compensation or honoraria from, Q State Biosciences. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Srivastava S., Love-Nichols J.A., Dies K.A., Ledbetter D.H., Martin C.L., Chung W.K., Firth H.V., Frazier T., Hansen R.L., Prock L., et al. NDD Exome Scoping Review Work Group Meta-analysis and multidisciplinary consensus statement: exome sequencing is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders. Genet. Med. 2019;21:2413–2421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Retterer K., Juusola J., Cho M.T., Vitazka P., Millan F., Gibellini F., Vertino-Bell A., Smaoui N., Neidich J., Monaghan K.G., et al. Clinical application of whole-exome sequencing across clinical indications. Genet. Med. 2016;18:696–704. - PubMed
-
- Posey J.E., O’Donnell-Luria A.H., Chong J.X., Harel T., Jhangiani S.N., Coban Akdemir Z.H., Buyske S., Pehlivan D., Carvalho C.M.B., Baxter S., et al. Centers for Mendelian Genomics Insights into genetics, human biology and disease gleaned from family based genomic studies. Genet. Med. 2019;21:798–812. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dragojlovic N., Elliott A.M., Adam S., van Karnebeek C., Lehman A., Mwenifumbo J.C., Nelson T.N., du Souich C., Friedman J.M., Lynd L.D. The cost and diagnostic yield of exome sequencing for children with suspected genetic disorders: a benchmarking study. Genet. Med. 2018;20:1013–1021. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

