Analysis of the gut microbiome in dogs and cats
- PMID: 34514619
- PMCID: PMC9292158
- DOI: 10.1111/vcp.13031
Analysis of the gut microbiome in dogs and cats
Abstract
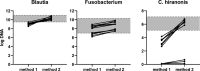
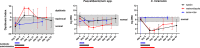
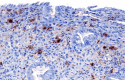
The gut microbiome is an important immune and metabolic organ. Intestinal bacteria produce various metabolites that influence the health of the intestine and other organ systems, including kidney, brain, and heart. Changes in the microbiome in diseased states are termed dysbiosis. The concept of dysbiosis is constantly evolving and includes changes in microbiome diversity and/or structure and functional changes (eg, altered production of bacterial metabolites). Molecular tools are now the standard for microbiome analysis. Sequencing of microbial genes provides information about the bacteria present and their functional potential but lacks standardization and analytical validation of methods and consistency in the reporting of results. This makes it difficult to compare results across studies or for individual clinical patients. The Dysbiosis Index (DI) is a validated quantitative PCR assay for canine fecal samples that measures the abundance of seven important bacterial taxa and summarizes the results as one single number. Reference intervals are established for dogs, and the DI can be used to assess the microbiome in clinical patients over time and in response to therapy (eg, fecal microbiota transplantation). In situ hybridization or immunohistochemistry allows the identification of mucosa-adherent and intracellular bacteria in animals with intestinal disease, especially granulomatous colitis. Future directions include the measurement of bacterial metabolites in feces or serum as markers for the appropriate function of the microbiome. This article summarizes different approaches to the analysis of gut microbiota and how they might be applicable to research studies and clinical practice in dogs and cats.
Keywords: Clostridium hiranonis; Dysbiosis Index; cats; dogs; fecal microbiota transplantation; metagenomics; microbiome.
© 2021 The Authors. Veterinary Clinical Pathology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The author is an employee of the Gastrointestinal Laboratory at Texas A&M University that offers microbiome and gastrointestinal function testing on a fee‐for‐service basis.
Figures

References
-
- Barry KA, Middelbos IS, Vester Boler BM, et al. Effects of dietary fiber on the feline gastrointestinal metagenome. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(12):5924‐5933. - PubMed
-
- Suchodolski JS, Morris EK, Allenspach K, et al. Prevalence and identification of fungal DNA in the small intestine of healthy dogs and dogs with chronic enteropathies. Vet Microbiol. 2008;132(3‐4):379‐388. - PubMed
-
- Ritchie LE, Steiner JM, Suchodolski JS. Assessment of microbial diversity along the feline intestinal tract using 16S rRNA gene analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2008;66(3):590‐598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

