Infant with Clefts Observation Outcomes Instrument (iCOO): A New Outcome for Infants and Young Children with Orofacial Clefts
- PMID: 34514868
- PMCID: PMC8918060
- DOI: 10.1177/10556656211040307
Infant with Clefts Observation Outcomes Instrument (iCOO): A New Outcome for Infants and Young Children with Orofacial Clefts
Abstract
Objective: We evaluated the measurement properties for item and domain scores of the Infant with Clefts Observation Outcomes Instrument (iCOO).
Design: Cross-sectional (before lip surgery) and longitudinal study (preoperative baseline and 2 days and 2 months after lip surgery).
Setting: Three academic craniofacial centers and national online advertisements.
Participants: Primary caregivers with an infant with cleft lip with or without cleft palate (CL ± P) scheduled to undergo primary lip repair. There were 133 primary caregivers at baseline, 115 at 2 days postsurgery, and 112 at 2 months postsurgery.
Main outcome measure(s): Caregiver observation items (n = 61) and global impression of health and function items (n = 8) across eight health domains.
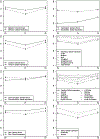
Results: Mean age at surgery was 6.0 months (range 2.7-11.8 months). Five of eight iCOO domains have scale scores, with Cronbach's alphas ranging from 0.67 to 0.87. Except for the Facial Skin and Mouth domain, iCOO scales had acceptable intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) ranging from 0.76 to 0.84. The internal consistency of the Global Impression items across all domains was 0.90 and had acceptable ICCs (range 0.76-0.91). Sixteen out of 20 (nonscale) items had acceptable ICCs (range 0.66-0.96). As anticipated, iCOO scores 2 days postoperatively were generally lower than baseline and scores 2 months postsurgery were consistent with baseline or higher. The iCOO took approximately 10 min to complete.
Conclusions: The iCOO meets measurement standards and may be used for assessing the impact of cleft-related treatments in clinical research and care. More research is needed on its use in various treatment contexts.
Keywords: cleft; infant; observer-reported outcome; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
None of the authors have conflicts of interest to report associated with this study.
Figures
References
-
- Bennett AV, Patrick DL, Lymp JF, Edwards TC, Goss CH. Comparison of 7-day and repeated 24-hour recall of symptoms of cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2010;9(6): 419–424. - PubMed
-
- Esenlik E, Gibson T, Kassam S, Sato Y, Garfinkle J et al. NAM therapy: Evidence-based results. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2020;57(4), 529–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials