Expanding the genetic spectrum of TUBB1-related thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 34516618
- PMCID: PMC8714720
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020004057
Expanding the genetic spectrum of TUBB1-related thrombocytopenia
Erratum in
-
Palma-Barqueros V, Bury L, Kunishima S, et al. Expanding the genetic spectrum of TUBB1-related thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2021;5(24):5453-5467.Blood Adv. 2023 Mar 28;7(6):877. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007189. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 36920438 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
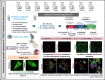
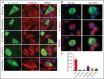
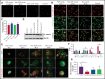
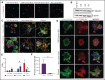
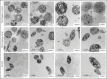
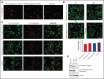
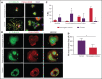
β1-Tubulin plays a major role in proplatelet formation and platelet shape maintenance, and pathogenic variants in TUBB1 lead to thrombocytopenia and platelet anisocytosis (TUBB1-RT). To date, the reported number of pedigrees with TUBB1-RT and of rare TUBB1 variants with experimental demonstration of pathogenicity is limited. Here, we report 9 unrelated families presenting with thrombocytopenia carrying 6 β1-tubulin variants, p.Cys12LeufsTer12, p.Thr107Pro, p.Gln423*, p.Arg359Trp, p.Gly109Glu, and p.Gly269Asp, the last of which novel. Segregation studies showed incomplete penetrance of these variants for platelet traits. Indeed, most carriers showed macrothrombocytopenia, some only increased platelet size, and a minority had no abnormalities. Moreover, only homozygous carriers of the p.Gly109Glu variant displayed macrothrombocytopenia, highlighting the importance of allele burden in the phenotypic expression of TUBB1-RT. The p.Arg359Trp, p.Gly269Asp, and p.Gly109Glu variants deranged β1-tubulin incorporation into the microtubular marginal ring in platelets but had a negligible effect on platelet activation, secretion, or spreading, suggesting that β1-tubulin is dispensable for these processes. Transfection of TUBB1 missense variants in CHO cells altered β1-tubulin incorporation into the microtubular network. In addition, TUBB1 variants markedly impaired proplatelet formation from peripheral blood CD34+ cell-derived megakaryocytes. Our study, using in vitro modeling, molecular characterization, and clinical investigations provides a deeper insight into the pathogenicity of rare TUBB1 variants. These novel data expand the genetic spectrum of TUBB1-RT and highlight a remarkable heterogeneity in its clinical presentation, indicating that allelic burden or combination with other genetic or environmental factors modulate the phenotypic impact of rare TUBB1 variants.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bastida JM, Benito R, Lozano ML, et al. . Molecular diagnosis of inherited coagulation and bleeding disorders. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2019;45(7): 695-707. - PubMed
-
- Savoia A. Molecular basis of inherited thrombocytopenias: an update. Curr Opin Hematol. 2016;23(5):486-492. - PubMed
-
- Balduini CL, Melazzini F, Pecci A. Inherited thrombocytopenias: recent advances in clinical and molecular aspects. Platelets. 2017;28(1):3-13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

