Prognostic impact of DNMT3A mutation in acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1
- PMID: 34516636
- PMCID: PMC8945292
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020004136
Prognostic impact of DNMT3A mutation in acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1
Erratum in
-
Oñate G, Bataller A, Garrido A, et al; CETLAM (Spanish Cooperative Group for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes). Prognostic impact of DNMT3A mutation in acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1. Blood Adv. 2022;6(3):882-890.Blood Adv. 2023 Mar 14;7(5):875. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009604. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 36917130 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
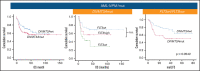
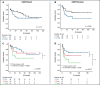
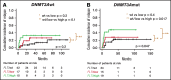
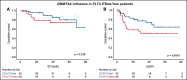
The negative prognostic impact of internal tandem duplication of FLT3 (FLT3-ITD) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1 (AML-NPM1) is restricted to those with a higher FLT3-ITD allelic ratio (FLT3high; ≥0.5) and considered negligible in those with a wild-type (FLT3WT)/low ITD ratio (FLT3low). Because the comutation of DNMT3A (DNMT3Amut) has been suggested to negatively influence prognosis in AML-NPM1, we analyzed the impact of DNMT3Amut in FLT3-ITD subsets (absent, low, and high ratios). A total of 164 patients diagnosed with AML-NPM1 included in 2 consecutive CETLAM protocols and with DNMT3A and FLT3 status available were studied. Overall, DNMT3Amut status did not have a prognostic impact, with comparable overall survival (P = .2). Prognostic stratification established by FLT3-ITD (FLT3WT = FLT3low > FLT3high) was independent of DNMT3Amut status. Measurable residual disease (MRD) based on NPM1 quantitative polymerase chain reaction was available for 94 patients. DNMT3Amut was associated with a higher number of mutated NPM1 transcripts after induction (P = .012) and first consolidation (C1; P < .001). All DNMT3Amut patients were MRD+ after C1 (P < .001) and exhibited significant MRD persistence after C2 and C3 (MRD+ vs MRD-; P = .027 and P = .001, respectively). Finally, DNMT3Amut patients exhibited a trend toward greater risk of molecular relapse (P = .054). In conclusion, DNMT3Amut did not modify the overall prognosis exerted by FLT3-ITD in AML-NPM1 despite delayed MRD clearance, possibly because of MRD-driven preemptive intervention.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bullinger L, Döhner K, Bair E, et al. Use of gene-expression profiling to identify prognostic subclasses in adult acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(16):1605-1616. - PubMed
-
- Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127(20):2391-2405. - PubMed
-
- Gale RE, Green C, Allen C, et al. ; Medical Research Council Adult Leukaemia Working Party . The impact of FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutant level, number, size, and interaction with NPM1 mutations in a large cohort of young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;111(5):2776-2784. - PubMed

