Circulating acetylated polyamines correlate with Covid-19 severity in cancer patients
- PMID: 34517343
- PMCID: PMC8457559
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203525
Circulating acetylated polyamines correlate with Covid-19 severity in cancer patients
Abstract
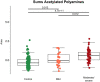
Cancer patients are particularly susceptible to the development of severe Covid-19, prompting us to investigate the serum metabolome of 204 cancer patients enrolled in the ONCOVID trial. We previously described that the immunosuppressive tryptophan/kynurenine metabolite anthranilic acid correlates with poor prognosis in non-cancer patients. In cancer patients, we observed an elevation of anthranilic acid at baseline (without Covid-19 diagnosis) and no further increase with mild or severe Covid-19. We found that, in cancer patients, Covid-19 severity was associated with the depletion of two bacterial metabolites, indole-3-proprionate and 3-phenylproprionate, that both positively correlated with the levels of several inflammatory cytokines. Most importantly, we observed that the levels of acetylated polyamines (in particular N1-acetylspermidine, N1,N8-diacetylspermidine and N1,N12-diacetylspermine), alone or in aggregate, were elevated in severe Covid-19 cancer patients requiring hospitalization as compared to uninfected cancer patients or cancer patients with mild Covid-19. N1-acetylspermidine and N1,N8-diacetylspermidine were also increased in patients exhibiting prolonged viral shedding (>40 days). An abundant literature indicates that such acetylated polyamines increase in the serum from patients with cancer, cardiovascular disease or neurodegeneration, associated with poor prognosis. Our present work supports the contention that acetylated polyamines are associated with severe Covid-19, both in the general population and in patients with malignant disease. Severe Covid-19 is characterized by a specific metabolomic signature suggestive of the overactivation of spermine/spermidine N1-acetyl transferase-1 (SAT1), which catalyzes the first step of polyamine catabolism.
Keywords: COVID-19; cancer; metabolomics; microbiota; polyamines.
Conflict of interest statement
AG, being part of the Drug Development Department (DITEP) at Gustave Roussy, has the following DITEP-relevant disclosures:
Principal/sub-Investigator of Clinical Trials for Abbvie, Adaptimmune, Adlai Nortye USA Inc, Aduro Biotech, Agios Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Argen-X Bvba, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Astra Zeneca Ab, Aveo, Basilea Pharmaceutica International Ltd, Bayer Healthcare Ag, Bbb Technologies Bv, Beigene, BicycleTx Ltd, Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ca, Celgene Corporation, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Clovis Oncology, Cullinan-Apollo, Curevac, Daiichi Sankyo, Debiopharm, Eisai, Eisai Limited, Eli Lilly, Exelixis, Faron Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Forma Tharapeutics, Gamamabs, Genentech, Glaxosmithkline, H3 Biomedicine, Hoffmann La Roche Ag, Imcheck Therapeutics, Innate Pharma, Institut De Recherche Pierre Fabre, Iris Servier, Iteos Belgium SA, Janssen Cilag, Janssen Research Foundation, Kura Oncology, Kyowa Kirin Pharm. Dev, Lilly France, Loxo Oncology, Lytix Biopharma As, Medimmune, Menarini Ricerche, Merck Sharp and Dohme Chibret, Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, Merus, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Molecular Partners Ag, Nanobiotix, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis Pharma, Octimet Oncology Nv, Oncoethix, Oncopeptides, Orion Pharma, Ose Pharma, Pfizer, Pharma Mar, Pierre Fabre, Medicament, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Seattle Genetics, Sotio A.S, Syros Pharmaceuticals, Taiho Pharma, Tesaro, Turning Point Therapeutics, Xencor.
Research Grants from Astrazeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, INCA, Janssen Cilag, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi.
Non-financial support (drug supplied) from Astrazeneca, Bayer, BMS, Boringher Ingelheim, GSK, Medimmune, Merck, NH TherAGuiX, Pfizer, Roche.
The authors declare that none of these activities are directly related to the present study.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

