A randomized controlled trial of stapled versus ultrasonic transection in distal pancreatectomy
- PMID: 34518950
- PMCID: PMC9085691
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-021-08724-3
A randomized controlled trial of stapled versus ultrasonic transection in distal pancreatectomy
Abstract
Background: The pancreatic transection method during distal pancreatectomy is thought to influence postoperative fistula rates. Yet, the optimal technique for minimizing fistula occurrence is still unclear. The present randomized controlled trial compared stapled versus ultrasonic transection in elective distal pancreatectomy.
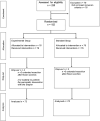
Methods: Patients undergoing distal pancreatectomy from July 2018 to July 2020 at two high-volume institutions were considered for inclusion. Exclusion criteria were contiguous organ resection and a parenchymal thickness > 17 mm on intraoperative ultrasound. Eligible patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to stapled transection (Endo GIA Reinforced Reload with Tri-Staple Technology®) or ultrasonic transection (Harmonic Focus® + or Harmonic Ace® + shears). The primary endpoint was postoperative pancreatic fistula. Secondary endpoints included overall complications, abdominal collections, and length of hospital stay.
Results: Overall, 72 patients were randomized in the stapled transection arm and 73 patients in the ultrasonic transection arm. Postoperative pancreatic fistula occurred in 23 patients (16%), with a comparable incidence between groups (12% in stapled transection versus 19% in ultrasonic dissection arm, p = 0.191). Overall complications did not differ substantially (35% in stapled transection versus 44% in ultrasonic transection arm, p = 0.170). There was an increased incidence of abdominal collections in the ultrasonic dissection group (32% versus 14%, p = 0.009), yet the need for percutaneous drain did not differ between randomization arms (p = 0.169). The median length of stay was 8 days in both groups (p = 0.880). Intraoperative blood transfusion was the only factor independently associated with postoperative pancreatic fistula on logistic regression analysis (OR 4.8, 95% CI 1.2-20.0, p = 0.032).
Conclusion: The present randomized controlled trial of stapled versus ultrasonic transection in elective distal pancreatectomy demonstrated no significant difference in postoperative pancreatic fistula rates and no substantial clinical impact on other secondary endpoints.
Keywords: Distal pancreatectomy; Pancreatic fistula; Stapler; Ultrasonic dissection.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Luca Landoni MD, Matteo De Pastena, Martina Fontana, Giuseppe Malleo, Alessandro Esposito, Luca Casetti, Giovanni Marchegiani, Massimiliano Tuveri, Antonio Pea, Marco Ramera, Alex Borin, Alessandro Giardino, Isabella Frigerio, Roberto Girelli, Claudio Bassi, Giovanni Butturini Roberto Salvia have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
References
-
- Diener MK, Seiler CM, Rossion I, Kleeff J, Glanemann M, Butturini G, Tomazic A, Bruns CJ, Busch ORC, Farkas S, Belyaev O, Neoptolemos JP, Halloran C, Keck T, Niedergethmann M, Gellert K, Witzigmann H, Kollmar O, Langer P, Steger U, Neudecker J, Berrevoet F, Ganzera S, Heiss MM, Luntz SP, Bruckner T, Kieser M, Büchler MW. Efficacy of stapler versus hand-sewn closure after distal pancreatectomy (DISPACT): a randomised, controlled multicentre trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2011;377:1514–1522. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60237-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sheehan MK, Beck K, Creech S, Pickleman J, Aranha GV. Distal pancreatectomy: does the method of closure influence fistula formation? Am Surg. 2002;68:264–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous