Advances and highlights in biomarkers of allergic diseases
- PMID: 34519063
- PMCID: PMC9292545
- DOI: 10.1111/all.15089
Advances and highlights in biomarkers of allergic diseases
Abstract
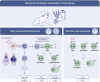
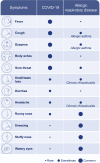
During the past years, there has been a global outbreak of allergic diseases, presenting a considerable medical and socioeconomical burden. A large fraction of allergic diseases is characterized by a type 2 immune response involving Th2 cells, type 2 innate lymphoid cells, eosinophils, mast cells, and M2 macrophages. Biomarkers are valuable parameters for precision medicine as they provide information on the disease endotypes, clusters, precision diagnoses, identification of therapeutic targets, and monitoring of treatment efficacies. The availability of powerful omics technologies, together with integrated data analysis and network-based approaches can help the identification of clinically useful biomarkers. These biomarkers need to be accurately quantified using robust and reproducible methods, such as reliable and point-of-care systems. Ideally, samples should be collected using quick, cost-efficient and noninvasive methods. In recent years, a plethora of research has been directed toward finding novel biomarkers of allergic diseases. Promising biomarkers of type 2 allergic diseases include sputum eosinophils, serum periostin and exhaled nitric oxide. Several other biomarkers, such as pro-inflammatory mediators, miRNAs, eicosanoid molecules, epithelial barrier integrity, and microbiota changes are useful for diagnosis and monitoring of allergic diseases and can be quantified in serum, body fluids and exhaled air. Herein, we review recent studies on biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of asthma, chronic urticaria, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, chronic rhinosinusitis, food allergies, anaphylaxis, drug hypersensitivity and allergen immunotherapy. In addition, we discuss COVID-19 and allergic diseases within the perspective of biomarkers and recommendations on the management of allergic and asthmatic patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; allergen immunotherapy; allergic diseases; biomarkers; precision medicine.
© 2021 The Authors. Allergy published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Ismail Ogulur, Yagiz Pat, Elena Barletta, Lacin Cevhertas, Ruben Fernandez‐Santamaria, Mengting Huang, Manal Bel Imam, Jana Koch, Siyuan Ma, Debbie J. Maurer, Yaqi Peng, Urszula Radzikowska, Arturo O. Rinaldi, Juan Rodriguez‐Coira, Pattraporn Satitsuksanoa, Stephan R. Schneider, Alexandra Wallimann, Damir Zhakparov, Reihane Ziadlou, Marie‐Charlotte Brüggen, Katja Baerenfaller, Luo Zhang, Mubeccel Akdis declare no conflict of interest. Yasutaka Mitamura and Willem van de Veen report grants from Novartis. Milena Sokolowska reports grants from Swiss National Science Foundation, GSK and Novartis. Cezmi Akdis reports grants from Allergopharma, Idorsia, Swiss National Science Foundation, Christine Kühne‐Center for Allergy Research and Education, European Commission's Horison's 2020 Framework Programme, Cure, Novartis Research Institutes, Basel, Astra Zeneca, Switzerland, Scibase, Stockholm, advisory role for Sanofi/Regeneron, Glaxo Smith‐Kline, Novartis.
Figures


References
-
- Yao Y, Chen CL, Yu D, Liu Z. Roles of follicular helper and regulatory T cells in allergic diseases and allergen immunotherapy. Allergy. 2021;76(2):456‐470. - PubMed
-
- Agache I, Akdis CA. Endotypes of allergic diseases and asthma: an important step in building blocks for the future of precision medicine. Allergol Int. 2016;65(3):243‐252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

