Predicting atrial fibrillation after cryptogenic stroke via a clinical risk score-a prospective observational study
- PMID: 34519135
- PMCID: PMC9292187
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.15102
Predicting atrial fibrillation after cryptogenic stroke via a clinical risk score-a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background and purpose: Atrial fibrillation (AF) often remains undiagnosed in cryptogenic stroke (CS), mostly because of limited availability of cardiac long-term rhythm monitoring. There is an unmet need for a pre-selection of CS patients benefitting from such work-up. A clinical risk score was therefore developed for the prediction of AF after CS and its performance was evaluated over 1 year of follow-up.
Methods: Our proposed risk score ranges from 0 to 16 points and comprises variables known to be associated with occult AF in CS patients including age, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, electrocardiographic and echocardiographic features (supraventricular premature beats, atrial runs, atrial enlargement, left ventricular ejection fraction) and brain imaging markers (multi-territory/prior cortical infarction). All CS patients admitted to our Stroke Unit between March 2018 and August 2019 were prospectively followed for AF detection over 1 year after discharge.
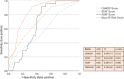
Results: During the 1-year follow-up, 24 (16%) out of 150 CS patients with AF (detected via electrocardiogram controls, n = 18; loop recorder monitoring, n = 6) were diagnosed. Our predefined AF Risk Score (cutoff ≥4 points; highest Youden's index) had a sensitivity of 92% and a specificity of 67% for 1-year prediction of AF. Notably, only two CS patients with <4 score points were diagnosed with AF later on (negative predictive value 98%).
Conclusions: A clinical risk score for 1-year prediction of AF in CS with high sensitivity, reasonable specificity and excellent negative predictive value is presented. Generalizability of our score needs to be tested in external cohorts with continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring.
Keywords: NT-proBNP; atrial fibrillation; biomarker; cryptogenic stroke; risk score.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gladstone DJ, Spring M, Dorian P, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2467‐2477. - PubMed
-
- Lip GYH, Banerjee A, Boriani G, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 2018;154:1121‐1201. - PubMed
-
- Hart RG, Sharma M, Mundl H, et al. Rivaroxaban for stroke prevention after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2191‐2201. - PubMed
-
- Diener HC, Sacco RL, Easton JD, et al., RE‐SPECT ESUS Steering Committee and Investigators. Dabigatran for prevention of stroke after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1906‐1917. - PubMed
-
- Diamantopoulos A, Sawyer LM, Lip GY, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of an insertable cardiac monitor to detect atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2016;11:302‐312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

