Target Discovery for Host-Directed Antiviral Therapies: Application of Proteomics Approaches
- PMID: 34519533
- PMCID: PMC8547474
- DOI: 10.1128/mSystems.00388-21
Target Discovery for Host-Directed Antiviral Therapies: Application of Proteomics Approaches
Abstract
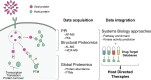
Current epidemics, such as AIDS or flu, and the emergence of new threatening pathogens, such as the one causing the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, represent major global health challenges. While vaccination is an important part of the arsenal to counter the spread of viral diseases, it presents limitations and needs to be complemented by efficient therapeutic solutions. Intricate knowledge of host-pathogen interactions is a powerful tool to identify host-dependent vulnerabilities that can be exploited to dampen viral replication. Such host-directed antiviral therapies are promising and are less prone to the development of drug-resistant viral strains. Here, we first describe proteomics-based strategies that allow the rapid characterization of host-pathogen interactions. We then discuss how such data can be exploited to help prioritize compounds with potential host-directed antiviral activity that can be tested in preclinical models.
Keywords: drug repurposing; host-directed therapies; host-pathogen interactions; proteomics; systems biology.
Figures
References
-
- Jackson LA, Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, Roberts PC, Makhene M, Coler RN, McCullough MP, Chappell JD, Denison MR, Stevens LJ, Pruijssers AJ, McDermott A, Flach B, Doria-Rose NA, Corbett KS, Morabito KM, O’Dell S, Schmidt SD, Swanson PA, Padilla M, Mascola JR, Neuzil KM, Bennett H, Sun W, Peters E, Makowski M, Albert J, Cross K, Buchanan W, Pikaart-Tautges R, Ledgerwood JE, Graham BS, Beigel JH, mRNA-1273 Study Group . 2020. An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 — preliminary report. N Engl J Med 383:1920–1931. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022483. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corbett KS, Edwards DK, Leist SR, Abiona OM, Boyoglu-Barnum S, Gillespie RA, Himansu S, Schäfer A, Ziwawo CT, DiPiazza AT, Dinnon KH, Elbashir SM, Shaw CA, Woods A, Fritch EJ, Martinez DR, Bock KW, Minai M, Nagata BM, Hutchinson GB, Wu K, Henry C, Bahl K, Garcia-Dominguez D, Ma L, Renzi I, Kong W-P, Schmidt SD, Wang L, Zhang Y, Phung E, Chang LA, Loomis RJ, Altaras NE, Narayanan E, Metkar M, Presnyak V, Liu C, Louder MK, Shi W, Leung K, Yang ES, West A, Gully KL, Stevens LJ, Wang N, Wrapp D, Doria-Rose NA, Stewart-Jones G, Bennett H, Alvarado GS, et al. . 2020. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 586:567–571. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2622-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sahin U, Muik A, Derhovanessian E, Vogler I, Kranz LM, Vormehr M, Baum A, Pascal K, Quandt J, Maurus D, Brachtendorf S, Lörks V, Sikorski J, Hilker R, Becker D, Eller A-K, Grützner J, Boesler C, Rosenbaum C, Kühnle M-C, Luxemburger U, Kemmer-Brück A, Langer D, Bexon M, Bolte S, Karikó K, Palanche T, Fischer B, Schultz A, Shi P-Y, Fontes-Garfias C, Perez JL, Swanson KA, Loschko J, Scully IL, Cutler M, Kalina W, Kyratsous CA, Cooper D, Dormitzer PR, Jansen KU, Türeci Ö. 2020. COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and T1 T cell responses. Nature 586:594–599. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2814-7. - DOI - PubMed
