Safety and Antibody Response After 1 and 2 Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
- PMID: 34519770
- PMCID: PMC8441592
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.26344
Safety and Antibody Response After 1 and 2 Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
Abstract
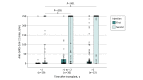
This cohort study examines safety and antibody responses after 1 and 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Humoral Immunity After mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Allogeneic HCT Recipients-Room for Improvement and Much to Learn.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Sep 1;4(9):e2127454. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27454. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34519771 No abstract available.
References
-
- García-Suárez J, de la Cruz J, Cedillo Á, et al. ; Asociación Madrileña de Hematología y Hemoterapia (AMHH) . Impact of hematologic malignancy and type of cancer therapy on COVID-19 severity and mortality: lessons from a large population-based registry study. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):133. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-00970-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xhaard A, Xhaard C, D’Aveni M, et al. . Risk factors for a severe form of COVID-19 after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a Société Francophone de Greffe de Moelle et de Thérapie cellulaire (SFGM-TC) multicentre cohort study. Br J Haematol. 2021;192(5):e121-e124. doi:10.1111/bjh.17260 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

