Discontinuation of anti-PD-1 monotherapy in advanced melanoma-Outcomes of daily clinical practice
- PMID: 34520567
- PMCID: PMC9293478
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.33800
Discontinuation of anti-PD-1 monotherapy in advanced melanoma-Outcomes of daily clinical practice
Abstract
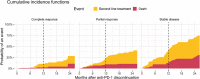
There is no consensus on the optimal treatment duration of anti-PD-1 for advanced melanoma. The aim of our study was to gain insight into the outcomes of anti-PD-1 discontinuation, the association of treatment duration with progression and anti-PD-1 re-treatment in relapsing patients. Analyses were performed on advanced melanoma patients in the Netherlands who discontinued first-line anti-PD-1 monotherapy in the absence of progressive disease (n = 324). Survival was estimated after anti-PD-1 discontinuation and with a Cox model the association of treatment duration with progression was assessed. At the time of anti-PD-1 discontinuation, 90 (28%) patients had a complete response (CR), 190 (59%) a partial response (PR) and 44 (14%) stable disease (SD). Median treatment duration for patients with CR, PR and SD was 11.2, 11.5 and 7.2 months, respectively. The 24-month progression-free survival and overall survival probabilities for patients with a CR, PR and SD were, respectively, 64% and 88%, 53% and 82%, 31% and 64%. Survival outcomes of patients with a PR and CR were similar when anti-PD-1 discontinuation was not due to adverse events. Having a PR at anti-PD-1 discontinuation and longer time to first response were associated with progression [hazard ratio (HR) = 1.81 (95% confidence interval, CI = 1.11-2.97) and HR = 1.10 (95% CI = 1.02-1.19; per month increase)]. In 17 of the 27 anti-PD-1 re-treated patients (63%), a response was observed. Advanced melanoma patients can have durable remissions after (elective) anti-PD-1 discontinuation.
Keywords: advanced melanoma; anti-PD-1; discontinuation; immunotherapy; real-world.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Alfons J. M. van den Eertwegh has received study grants for Sanofi, Roche, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, TEVA, Idera; travel expenses from MSD Oncology, Roche, Pfizer, Sanofi; speaker honoraria from Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Novartis; advisory relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Amgen, Roche, Novartis, Sanofi, Pfizer, Ipsen, Merck and Pierre Fabre. Jan‐Willem B. de Groot has advisory relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, MSD, Pierre Fabre, Servier. Geke A. P. Hospers has advisory relationships with MSD, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Novartis; received research grant from Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Seerave. Karijn P. M. Suijkerbuijk has advisory relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Novartis, MSD, Pierre Fabre, Abbvie; received honoraria from MSD, Roche and Novartis. Astrid A.M. van der Veldt has consultancy relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, MSD, Merck, Eisai, Sanofi, Pfizer, Novartis, Ipsen, Roche. John B. A. G. Haanen has advisory relationships with Achilles Tx, BioNTech, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Immunocore, MSD, Merck Serono, Molecular Partners, Novartis, Pfizer, PokeAcel, Roche, Sanofi, T‐Knife, Third Rock Ventures, Neogene Tx (including stock options); received research grants from Asher Bio, Amgen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, BioNTech, MSD, Novartis. Maureen J. B. Aarts has advisory relationships with Amgen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Novartis, MSD, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Pfizer, Ipsen, Merck, Astellas; received research grants from Pfizer. All grants/fees were not related to this article and paid to the institutions. The funders had no role in the writing of this article or decision to submit it for publication. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open‐label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE‐006). Lancet. 2017;390:1853‐1862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

