Medium- to long-term clinical and functional outcomes of isolated and combined subscapularis tears repaired arthroscopically
- PMID: 34522265
- PMCID: PMC8425253
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2020.97714
Medium- to long-term clinical and functional outcomes of isolated and combined subscapularis tears repaired arthroscopically
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was twofold. First, the efficacy of arthroscopic repair in patients with full thickness, isolated subscapularis tendon tears (I-STTs) or combined subscapularis tendon tears (C-STTs) involving the rotator cuff tendons was evaluated. Second, the outcomes between these two groups were compared. The influence of age and gender on the cohort clinical outcomes was also analysed. Our hypothesis was that satisfactory functional results could be obtained arthroscopically in both groups without any influence of age or gender.
Material and methods: Seventy-nine patients were enrolled: 15 with I-STTs and 64 with C-STTs. The clinical outcomes were assessed using Constant and Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) scores, Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) for pain and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for satisfaction. The subscapularis strength was assessed using a comparative dynamometric bear-hug test. Group outcomes were compared, including statistical analysis.
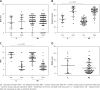
Results: For each group, there were no differences regarding the subscapularis strength of the operated and non-operated shoulders. A comparison of the post- with the pre-operative outcomes showed an increase in the Constant score and a decrease in the NRS. Comparing the two groups, we found no difference in strength of the operated and non-operated shoulders, but a significant difference in relation to pre-operative Constant score and pre-operative NRS. Age was negatively correlated with both pre-operative and post-operative Constant scores. No association was found between gender and the outcomes, although the DASH score was higher in women.
Conclusions: Arthroscopic repair of STTs provided functional restoration, pain relief and patient satisfaction in both groups. Age and gender did not affect the clinical outcomes achieved by arthroscopic STT repair.
Keywords: Constant score; arthroscopy; rotator cuff; subscapularis repair; subscapularis tendon tears.
Copyright: © 2020 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Keating JF, Waterworth P, Shaw-Dunn J, Crossan J. The relative strengths of the rotator cuff muscles. A cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:137–40. - PubMed
-
- Deutsch A, Altchek DW, Veltri DM, Potter HG, Warren RF. Traumatic tears of the subscapularis tendon. Clinical diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging findings, and operative treatment. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25:13–22. - PubMed
-
- Arai R, Sugaya H, Mochizuki T, Nimura A, Moriishi J, Akita K. Subscapularis tendon tear: an anatomic and clinical investigation. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:997–1004. - PubMed
-
- Adams CR, Schoolfield JD, Burkhart SS. Accuracy of pre-operative magnetic resonance imaging in predicting a subscapularis tendon tear based on arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1427–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
