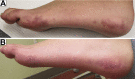
Atypical presentation of pediatric antiphospholipid syndrome
- PMID: 34522747
- PMCID: PMC8426164
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.07.033
Atypical presentation of pediatric antiphospholipid syndrome
Keywords: APS, antiphospholipid syndrome; DRVVT, dilute Russell viper venom time; EAH, eccrine angiomatous hamartoma; LR, livedo reticularis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; anti-cardiolipin; antiphospholipid syndrome; beta-2-glycoprotein; eccrine angiomatous hamartoma; hypercoagulable.
Conflict of interest statement
None disclosed.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
