Duration of carriage of multidrug-resistant bacteria in dogs and cats in veterinary care and co-carriage with their owners
- PMID: 34522760
- PMCID: PMC8424212
- DOI: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100322
Duration of carriage of multidrug-resistant bacteria in dogs and cats in veterinary care and co-carriage with their owners
Abstract
Background: The emergence and spread of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) represent a threat to human and animal health.
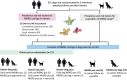
Objectives: To assess duration of carriage of MDROs in dogs and cats presented to veterinary clinics/hospitals in Switzerland. To estimate prevalence, duration of and risk factors for MDRO carriage in their owners and the occurrence of co-carriage in owner-pet pairs.
Methods: Prospective, longitudinal, observational study. Nasal swabs and fecal samples were collected from 50 owners of dogs and cats presented to 3 large veterinary hospitals, 1 medium-sized clinic and 1 practice. If pet or owner tested positive for a MDRO, follow-up samples were collected for up to 8 months. Methicillin-resistant (MR) Staphylococcus aureus, MR S. pseudintermedius, MR coagulase-negative staphylococci (MRCoNS), MR Macrococcus spp., cephalosporinase- and carbapenemase-producing (CP) Enterobacterales were isolated and further characterized by MALDI-TOF MS, microdilution, β-lactam resistance gene detection, REP/ERIC-PCR, multilocus sequence typing or whole-genome sequencing. Risk factors for MDRO carriage in owners were explored based on questionnaire-derived data.
Results: Five out of 50 owners carried 3rd generation cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales (3GC-R-Ent.), and 5/50 MRCoNS. In 3 dogs and 4 cats carriage of 3GC-R-Ent. persisted for up to 136 days after discharge (median 99 days, IQR 83 days, range 36-136 days), in two cats isolates were carbapenem-resistant. Owner-pet co-carriage was not observed. No specific risk factors for MDRO carriage in owners were identified.
Conclusions: After discharge from veterinary care, dogs and cats may carry 3GC-R-Ent. for prolonged time periods. Carriage of MDROs was common in owners, but pet-owner co-carriage of the same MDRO was not observed.
Keywords: 3GC-R, Third Generation Cephalosporin-resistant; 3GC-R-Ent., Third Generation Cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales; AMR, Antimicrobial resistance; CI, Confidence interval; CLSI, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; COL-R, Colistin-resistant; CP, Carbapenemase-producing; CR, Carbapenem-resistant; CRE, Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales; Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales; Co-carriage; Companion animal; ERIC-PCR, Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus polymerase chain reaction; ESBL, Extended spectrum β-lactamase; ESBL-E. coli, ESBL-producing Escherichia coli; ESBL-KP, ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae; EUCAST, European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Extended-spectrum β-lactamase; IQR, Interquartile range; KP, Klebsiella pneumoniae; MALDI-TOF MS, Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry; MDR, Multidrug-resistant; MDROs, Multidrug-resistant organisms; MICs, Minimal inhibitory concentrations; MLST, Multilocus sequence typing; MR, Methicillin-resistant; MRCoNS, Methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci; MRSA, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MRSP, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius; REP-PCR, Repetitive element palindromic polymerase chain reaction; ST, Sequence type; TMP-S, Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole; Transmission; WGS, Whole-genome sequencing; pAmpC, Plasmid-encoded AmpC.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

 Presentation □ Discharge ○ Follow-up Antimicrobial treatments
Presentation □ Discharge ○ Follow-up Antimicrobial treatments  Potentiated aminopenicillins
Potentiated aminopenicillins  Fluoroquinolones Abbreviations: CP: carbapenemase-producing; ESBL: extended spectrum β-lactamase-producing; E. coli: Escherichia coli; KP: Klebsiella pneumoniae; E. cloacae: Enterobacter cloacae; MR: Methicillin-resistant; S.: Staphylococcus
Fluoroquinolones Abbreviations: CP: carbapenemase-producing; ESBL: extended spectrum β-lactamase-producing; E. coli: Escherichia coli; KP: Klebsiella pneumoniae; E. cloacae: Enterobacter cloacae; MR: Methicillin-resistant; S.: Staphylococcus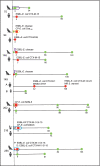
 Presentation □ Discharge ○ Follow-up Antimicrobial treatments
Presentation □ Discharge ○ Follow-up Antimicrobial treatments  First generation cephalosporin
First generation cephalosporin  Potentiated aminopenicillin
Potentiated aminopenicillin  Fluoroquinolone
Fluoroquinolone  Clindamycin + trimethoprim+sulphamethoxazole
Clindamycin + trimethoprim+sulphamethoxazole  Perioperative cefazolin
Perioperative cefazolinReferences
-
- Magiorakos A.P., Srinivasan A., Carey R.B., Carmeli Y., Falagas M.E., Giske C.G., et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012;18:268–281. - PubMed
-
- McNicholas J., Gilbey A., Rennie A., Ahmedzai S., Dono J.-A., Ormerod E. Pet ownership and human health: a brief review of evidence and issues. BMJ. 2005;331(7527):1252–1254. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16308387 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedmann E., Son H. The human-companion animal bond: how humans benefit. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009;39:293–326. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19185195/ - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

