Chemerin regulates normal angiogenesis and hypoxia-driven neovascularization
- PMID: 34524600
- PMCID: PMC9054887
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-021-09818-1
Chemerin regulates normal angiogenesis and hypoxia-driven neovascularization
Abstract
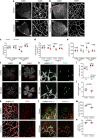
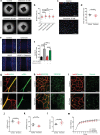
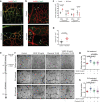
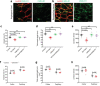
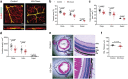
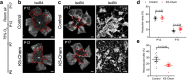
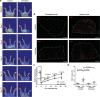
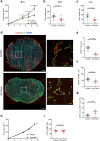
Chemerin is a multifunctional protein initially characterized in our laboratory as a chemoattractant factor for leukocyte populations. Its main functional receptor is CMKLR1. We identified previously chemerin as an anti-tumoral factor inhibiting the vascularization of tumor grafts. We show here that overexpression of bioactive chemerin in mice results in a reduction of the density of the retinal vascular network during its development and in adults. Chemerin did not affect vascular sprouting during the post-natal development of the network, but rather promoted endothelial cell apoptosis and vessel pruning. This phenotype was reversed to normal in CMKLR1-deficient mice, demonstrating the role of this receptor. Chemerin inhibited also neoangiogenesis in a model of pathological proliferative retinopathy, and in response to hind-limb ischemia. Mechanistically, PTEN and FOXO1 antagonists could almost completely restore the density of the retinal vasculature, suggesting the involvement of the PI3-kinase/AKT pathway in the chemerin-induced vessel regression process.
Keywords: CMKLR1; ChemR23; Hind-limb ischemia model; Oxygen-induced retinopathy; Retinal angiogenesis; Tumoral neoangiogenesis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.P. is C.E.O. of the biotech company Gepeceron. All other authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

