Do age, fitness, and concomitant medications influence management and outcomes of patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib?
- PMID: 34525181
- PMCID: PMC8714729
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004824
Do age, fitness, and concomitant medications influence management and outcomes of patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib?
Abstract
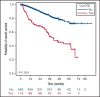
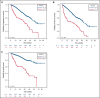
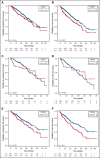
Functional reserve of organs and systems is known to be relevant in predicting immunochemotherapy tolerance. Age and comorbidities, assessed by the cumulative illness rating scale (CIRS), have been used to address chemotherapy intensity. In the ibrutinib era, it is still unclear whether age, CIRS, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG-PS) retain their predictive role on treatment vulnerability. In this series of 712 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with ibrutinib outside clinical trials, baseline ECOG-PS and neutropenia resulted as the most accurate predictors of treatment feasibility and outcomes. Age did not independently influence survival and ibrutinib tolerance, indicating that not age per se, but age-related conditions, may affect drug management. We confirmed the role of CIRS > 6 as a predictor of a poorer progression- and event-free survival (PFS, EFS). The presence of a severe comorbidity was significantly associated with permanent dose reductions (PDRs), not translating into worse outcomes. As expected, del(17p) and/or TP53mut and previous therapies affected PFS, EFS, and overall survival. No study so far has analyzed the influence of concomitant medications and CYP3A inhibitors with ibrutinib. In our series, these factors had no impact, although CYP3A4 inhibitors use correlated with Cox regression analysis, with an increased risk of PDR. Despite the limitation of its retrospective nature, this large study confirmed the role of ECOG-PS as the most accurate predictor of ibrutinib feasibility and outcomes, and importantly, neutropenia emerged as a relevant tool influencing patients' vulnerability. Although CIRS > 6 retained a significant impact on PFS and EFS, its value should be confirmed by prospective studies.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- SEER. Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/. Accessed 25 May 2020.
-
- Stauder R, Eichhorst B, Hamaker ME, et al. . Management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in the elderly: a position paper from an international Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) Task Force. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(2):218-227. - PubMed
-
- Eichhorst B, Hallek M, Goede V. Management of unfit elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;58:7-13. - PubMed
-
- Eichhorst B, Fink AM, Bahlo J, et al. ; German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) . First-line chemoimmunotherapy with bendamustine and rituximab versus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL10): an international, open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(7):928-942. - PubMed
-
- Goede V, Fischer K, Busch R, et al. . Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in patients with CLL and coexisting conditions. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(12):1101-1110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

