Harnessing features of adaptive NK cells to generate iPSC-derived NK cells for enhanced immunotherapy
- PMID: 34525347
- PMCID: PMC8642276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.08.013
Harnessing features of adaptive NK cells to generate iPSC-derived NK cells for enhanced immunotherapy
Abstract
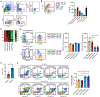
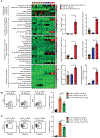
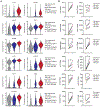
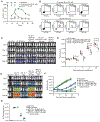
Select subsets of immune effector cells have the greatest propensity to mediate antitumor responses. However, procuring these subsets is challenging, and cell-based immunotherapy is hampered by limited effector-cell persistence and lack of on-demand availability. To address these limitations, we generated a triple-gene-edited induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC). The clonal iPSC line was engineered to express a high affinity, non-cleavable version of the Fc receptor CD16a and a membrane-bound interleukin (IL)-15/IL-15R fusion protein. The third edit was a knockout of the ecto-enzyme CD38, which hydrolyzes NAD+. Natural killer (NK) cells derived from these uniformly engineered iPSCs, termed iADAPT, displayed metabolic features and gene expression profiles mirroring those of cytomegalovirus-induced adaptive NK cells. iADAPT NK cells persisted in vivo in the absence of exogenous cytokine and elicited superior antitumor activity. Our findings suggest that unique subsets of the immune system can be modeled through iPSC technology for effective treatment of patients with advanced cancer.
Keywords: NK cell; acute myeloid leukemia; adaptive; iPSC; immunotherapy; induced pluripotent stem cell; multiple myeloma; natural killer cell; off-the-shelf.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests F.C. and J.S.M. are paid consultants for Fate Therapeutics, and they receive research funds from this relationship. J.S.M. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board of OnkImmune, Nektar, Magenta and is a paid consultant consult for GT BioPharma and Vycellix (all unrelated to the content of this manuscript). He receives research funds from these relationships. B.R.B is a paid consultant/advisor for Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Obsidian Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bluerock. He receives research support from Tmunity, Bluerock, Kadmon, and Rheos and is co-founder of Tmunity. None of these relationships conflict with the content of the published research. He also receives research support from Fate Therapeutics for research unrelated to the content of this report. R.B., S.G., S.M., R.A., P.R., M.Q.G., G.B., M.M., J.H., T.D., T.T.L., and B.V. are employees of Fate Therapeutics. Fate Therapeutics owns patents (Methods and compositions for inducing hematopoietic cell differentiation; patent: 10,626,372) covering the iPSC-derived NK cells.
Figures



Comment in
-
Into the multiverse of gene edited NK cell-based therapeutic strategies.Cell Stem Cell. 2021 Dec 2;28(12):2041-2043. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.11.004. Cell Stem Cell. 2021. PMID: 34861144
References
-
- Bachanova V, Cooley S, Defor TE, Verneris MR, Zhang B, McKenna DH, Curtsinger J Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Lewis D, Hippen K, et al. (2014). Clearance of acute myeloid leukemia by haploidentical natural killer cells is improved using IL-2 diphtheria toxin fusion protein. Blood. 123, 3855–3862. 10.1182/blood-2013-10-532531. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brentjens RJ, Rivière I, Park JH, Davila MJ, Wang X, Stefanski J, Taylor C, Yeh R, Bartido S, Borquez-Ojeda O, et al. (2011). Safety and persistence of adoptively transferred autologous CD19-targeted T cells in patients with relapsed or chemotherapy refractory B-cell leukemias. Blood. 118, 4817–4828. 10.1182/blood-2011-04-348540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casneuf T, Xu XS, Adams HC 3rd, Axel AE, Chiu C, Khan I, Ahmadi T, Yan X, Lonial S, Plesner T, et al. (2017). Effects of daratumumab on natural killer cells and impact on clinical outcomes in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 1, 2105–2114. 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017006866. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

