GLP-1 receptor agonists and cardiorenal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an updated meta-analysis of eight CVOTs
- PMID: 34526024
- PMCID: PMC8442438
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-021-01366-8
GLP-1 receptor agonists and cardiorenal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an updated meta-analysis of eight CVOTs
Abstract
Background: A meta-analysis is presented of cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs) comparing glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) versus placebo on cardiorenal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
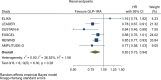
Methods: We did an electronic search up to June 30, 2021, for eligible trials. We did a meta-analysis of available trial data using a random-effects model to calculate overall hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CI (confidence intervals). We included data from 8 CVOTs and 60,080 patients (72.4% with established cardiovascular disease).
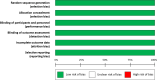
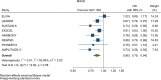
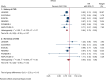
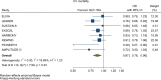
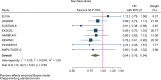
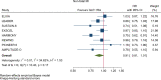
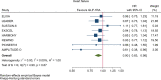
Results: GLP-1RA reduced major cardiovascular events (MACE) by 14% (HR = 0.86, 95% CI 0.79-0.94, P = 0.006) with a non-significant heterogeneity between subgroups of patients with and without cardiovascular disease (P = 0.127). GLP-1RA also reduced the risk of cardiovascular death by 13% (P = 0.016), nonfatal stroke by 16% (P = 0.007), hospitalization for heart failure by 10% (P = 0.023), all-cause mortality by 12% (P = 0.012), and the broad composite kidney outcome by 17% (P = 0.012), which was driven by a reduction in macroalbuminuria only (HR = 0.74, 0.67-0.82, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: GLP-1RA have moderate benefits on MACE, and also reduce hospitalization for heart failure and all-cause mortality; they also have robust benefits on reducing the incidence of macroalbuminuria.
Keywords: Albiglutide; Cardiorenal outcomes; Cardiovascular outcome trials; Dulaglutide; Efpeglenatide; Exenatide; GLP-1RA; Liraglutide; Lixisenatide; Oral semaglutide; Semaglutide; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D. G. received a consultancy fee from Eli Lilly and has held lectures for Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Mundipharma, Sanofi. M. I. M. has held lectures for Astrazeneca, Sanofi, NovoNordisk, and MSD. K. E. received a consultancy fee from Eli Lilly and has held lectures for Eli Lilly, Sanofi, and Novo Nordisk. A.C. has been an advisory board member for Abbott, Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, DOC Generici, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk and OM Pharma; has given lectures for Astra Zeneca, Berlin Chemie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk and Roche Diagnostics; and has received research grants from Astra Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Mitsubishi and Novartis. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, et al. Comparison of the effects of glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus—systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcomes trials. Circulation. 2019;139:2022–2031. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038868. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Giugliano D, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Chiodini P, Esposito G. Glycemic control, pre-existing cardiovascular disease and risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials vs intensive glucose control trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e012356. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012356. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giugliano D, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Longo M, Chiodini P, Esposito K. GLP-1 receptor agonists for prevention of cardiorenal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an updated meta-analysis including the REWIND and PIONEER 6 trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21:2576–2580. doi: 10.1111/dom.13847. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

