The MAGNOLIA Trial: Zanubrutinib, a Next-Generation Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Demonstrates Safety and Efficacy in Relapsed/Refractory Marginal Zone Lymphoma
- PMID: 34526366
- PMCID: PMC9401507
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1704
The MAGNOLIA Trial: Zanubrutinib, a Next-Generation Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Demonstrates Safety and Efficacy in Relapsed/Refractory Marginal Zone Lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) is an uncommon non-Hodgkin lymphoma with malignant cells that exhibit a consistent dependency on B-cell receptor signaling. We evaluated the efficacy and safety of zanubrutinib, a next-generation selective Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MZL.
Patients and methods: Patients with R/R MZL were enrolled in the phase II MAGNOLIA (BGB-3111-214) study. The primary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) as determined by an independent review committee (IRC) based on the Lugano 2014 classification.
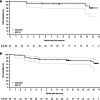
Results: Sixty-eight patients were enrolled. After a median follow-up of 15.7 months (range, 1.6 to 21.9 months), the IRC-assessed ORR was 68.2% and complete response (CR) was 25.8%. The ORR by investigator assessment was 74.2%, and the CR rate was 25.8%. The median duration of response (DOR) and median progression-free survival (PFS) by independent review was not reached. The IRC-assessed DOR rate at 12 months was 93.0%, and IRC-assessed PFS rate was 82.5% at both 12 and 15 months. Treatment was well tolerated with the majority of adverse events (AE) being grade 1 or 2. The most common AEs were diarrhea (22.1%), contusion (20.6%), and constipation (14.7%). Atrial fibrillation/flutter was reported in 2 patients; 1 patient had grade 3 hypertension. No patient experienced major hemorrhage. In total, 4 patients discontinued treatment due to AEs, none of which were considered treatment-related by the investigators.
Conclusions: Zanubrutinib demonstrated high ORR and CR rate with durable disease control and a favorable safety profile in patients with R/R MZL.
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


Comment on
-
Selected Articles from This Issue.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 1;27(23):6279. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-27-23-HI. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34853073 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kahl B, Yang D. Marginal zone lymphomas: management of nodal, splenic, and MALT NHL. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2008;359–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

