Structure-based classification predicts drug response in EGFR-mutant NSCLC
- PMID: 34526717
- PMCID: PMC8481125
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03898-1
Structure-based classification predicts drug response in EGFR-mutant NSCLC
Abstract
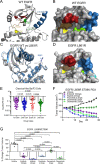
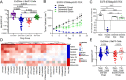
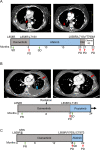
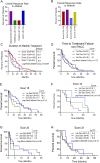
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations typically occur in exons 18-21 and are established driver mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)1-3. Targeted therapies are approved for patients with 'classical' mutations and a small number of other mutations4-6. However, effective therapies have not been identified for additional EGFR mutations. Furthermore, the frequency and effects of atypical EGFR mutations on drug sensitivity are unknown1,3,7-10. Here we characterize the mutational landscape in 16,715 patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC, and establish the structure-function relationship of EGFR mutations on drug sensitivity. We found that EGFR mutations can be separated into four distinct subgroups on the basis of sensitivity and structural changes that retrospectively predict patient outcomes following treatment with EGFR inhibitors better than traditional exon-based groups. Together, these data delineate a structure-based approach for defining functional groups of EGFR mutations that can effectively guide treatment and clinical trial choices for patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC and suggest that a structure-function-based approach may improve the prediction of drug sensitivity to targeted therapies in oncogenes with diverse mutations.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The research being reported in this publication is research in which The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center has an institutional financial conflict of interest. Because MD Anderson is committed to the protection of human subjects and the effective management of its financial conflicts of interest in relation to its research activities, MD Anderson has implemented an Institutional Conflict of Interest Management and Monitoring Plan to manage and monitor the conflict of interest with respect to MD Anderson’s conduct of this research. MD Anderson, including J.P.R., M.B.N. and J.V.H. have filed a patent for the use of poziotinib for treating EGFR- and HER2-mutant cancers and licensed the technology to Spectrum Pharmaceuticals. J.P.R. and J.V.H. receive research support from Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Takeda and Enliven Therapeutics. MD Anderson, including M.B.N., J.P.R. and J.V.H. have a pending patent submitted for treatment of EGFR TKI resistant NSCLC, and another, including J.P.R., S.H. and J.V.H., for the classification of EGFR mutations. J.P.R. and M.B.N. have no non-financial competing interests. J.V.H. also receives grant or research support from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline and has served on advisory committees for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Catalyst, EMD Serono, Foundation Medicine (FMI), Hengrui Therapeutics, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Guardant Health, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Takeda. As non-financial competing interests, J.V.H. serves as scientific advisor for Rexanna Foundation and the EGFR resisters. X. Le receives consulting/advisory fees from EMD Serono (Merck KGaA), AstraZeneca, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Hengrui Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, and Celgene, and research funding to the institution from Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim, and no non-financial competing interests. Y.Y.E. discloses research support from Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Xcovery, Turning Point Therapeutics; advisory role for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Turning Point Therapeutics; and accommodation expenses from Eli Lilly, and no non-financial competing interests. J.Z. reports research funding and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Geneplus, OrigMed, Innovent, Merck, Johnson and Johnson, and no non-financial competing interests. F.S. receives consulting/advisory fees from Amgen, Navire Pharma, Intellisphere LLC; research funding to the institution from Amgen, Mirati Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck&Co, Novartis, Pfizer; speaker’s fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb and RV Mais Promocao Eventos LTDS; other support from AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals; travel expenses from Tango Therapeutics and reports past stock ownership of Moderna Inc and BioNTech SE. As non-financial competing interests F.S. serves as scientific advisor for Tango Therapeutics and has previously served as advisor for Calithera Biosciences. J.E.G. reports research support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, G1 Therapeutics, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and the Lurdwig Institute of Cancer Research, and serves as a consultant/advisor for Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen, Novartis, Merck, Inivata, EMD Serono, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Blueprint Medicines, and AstraZeneca. H.T. reports research support from Bayer AS, Guardant Health, Ziopharm, and no non-financial interests. J.S. and V.R. are shareholders/full time employees of Guardant Health and report no non-financial interests. R.M. and A.B.S. are full time employees of Foundation medicine, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Roche, and have Roche stock ownership, with no non-financial competing interests. J.K.H. receives research support from OneOme, is a consultant for Quest Diagnostics and 23andMe, and has served on an advisory committee for Novartis, and has provided educational content for the American College of Clinical Pharmacy, Florida Pharmacy Association and HorizonCME. All other authors report no financial or non-financial competing interests.
Figures











Comment in
-
Structure-based classification of EGFR mutations informs inhibitor selection for lung cancer therapy.Cancer Cell. 2021 Nov 8;39(11):1455-1457. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.10.012. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Cancer Cell. 2021. PMID: 34752753 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting more precisely: Improving sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in NSCLC.Med. 2021 Nov 12;2(11):1201-1202. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2021.10.005. Med. 2021. PMID: 35590196
References
-
- Russo A, et al. Heterogeneous responses to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with uncommon EGFR mutations: new insights and future perspectives in this complex clinical scenario. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:1431. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061431. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

