CARes-UNet: Content-aware residual UNet for lesion segmentation of COVID-19 from chest CT images
- PMID: 34528263
- PMCID: PMC8646636
- DOI: 10.1002/mp.15231
CARes-UNet: Content-aware residual UNet for lesion segmentation of COVID-19 from chest CT images
Abstract
Purpose: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused a serious global health crisis. It has been proven that the deep learning method has great potential to assist doctors in diagnosing COVID-19 by automatically segmenting the lesions in computed tomography (CT) slices. However, there are still several challenges restricting the application of these methods, including high variation in lesion characteristics and low contrast between lesion areas and healthy tissues. Moreover, the lack of high-quality labeled samples and large number of patients lead to the urgency to develop a high accuracy model, which performs well not only under supervision but also with semi-supervised methods.
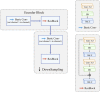
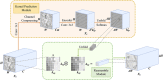
Methods: We propose a content-aware lung infection segmentation deep residual network (content-aware residual UNet (CARes-UNet)) to segment the lesion areas of COVID-19 from the chest CT slices. In our CARes-UNet, the residual connection was used in the convolutional block, which alleviated the degradation problem during the training. Then, the content-aware upsampling modules were introduced to improve the performance of the model while reducing the computation cost. Moreover, to achieve faster convergence, an advanced optimizer named Ranger was utilized to update the model's parameters during training. Finally, we employed a semi-supervised segmentation framework to deal with the problem of lacking pixel-level labeled data.
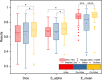
Results: We evaluated our approach using three public datasets with multiple metrics and compared its performance to several models. Our method outperforms other models in multiple indicators, for instance in terms of Dice coefficient on COVID-SemiSeg Dataset, CARes-UNet got the score 0.731, and semi-CARes-UNet further boosted it to 0.776. More ablation studies were done and validated the effectiveness of each key component of our proposed model.
Conclusions: Compared with the existing neural network methods applied to the COVID-19 lesion segmentation tasks, our CARes-UNet can gain more accurate segmentation results, and semi-CARes-UNet can further improve it using semi-supervised learning methods while presenting a possible way to solve the problem of lack of high-quality annotated samples. Our CARes-UNet and semi-CARes-UNet can be used in artificial intelligence-empowered computer-aided diagnosis system to improve diagnostic accuracy in this ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: computed tomography (CT) image; content-aware residual UNet; coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); deep learning; segmentation.
© 2021 American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

