Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status - 13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4-July 17, 2021
- PMID: 34529637
- PMCID: PMC8445374
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7037e1
Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status - 13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4-July 17, 2021
Abstract
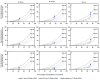
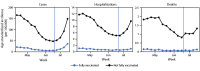
COVID-19 vaccine breakthrough infection surveillance helps monitor trends in disease incidence and severe outcomes in fully vaccinated persons, including the impact of the highly transmissible B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Reported COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths occurring among persons aged ≥18 years during April 4-July 17, 2021, were analyzed by vaccination status across 13 U.S. jurisdictions that routinely linked case surveillance and immunization registry data. Averaged weekly, age-standardized incidence rate ratios (IRRs) for cases among persons who were not fully vaccinated compared with those among fully vaccinated persons decreased from 11.1 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 7.8-15.8) to 4.6 (95% CI = 2.5-8.5) between two periods when prevalence of the Delta variant was lower (<50% of sequenced isolates; April 4-June 19) and higher (≥50%; June 20-July 17), and IRRs for hospitalizations and deaths decreased between the same two periods, from 13.3 (95% CI = 11.3-15.6) to 10.4 (95% CI = 8.1-13.3) and from 16.6 (95% CI = 13.5-20.4) to 11.3 (95% CI = 9.1-13.9). Findings were consistent with a potential decline in vaccine protection against confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and continued strong protection against COVID-19-associated hospitalization and death. Getting vaccinated protects against severe illness from COVID-19, including the Delta variant, and monitoring COVID-19 incidence by vaccination status might provide early signals of changes in vaccine-related protection that can be confirmed through well-controlled vaccine effectiveness (VE) studies.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. Janelle Delgadillo reports grant support from the Utah Department of Health. Ruth Lynfield reports that she is president of the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists, Secretary of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases, and Associate Editor of the American Academy of Pediatrics Red Book (the fee for which is donated to the Minnesota Department of Health). Rachel K. Herlihy reports funding from the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists for travel to meetings and conferences. No other potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Guidance on conducting vaccine effectiveness evaluations in the setting of new SARS-CoV-2 variants: interim guidance, 22 July 2021. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccine_effectiven...
-
- Havers FP, Pham H, Taylor CA, et al. COVID-19–associated hospitalizations among vaccinated and unvaccinated adults ≥18 years—COVID-NET, 13 states, January 1–July 24, 2021. medRxiv [Preprint posted online August 29, 2021]. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08.27.21262356v1 - DOI
-
- Fowlkes A, Gaglani M, Groover K, Thiese MS, Tyner H, Ellingson K; HEROES-RECOVER Cohorts. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among frontline workers before and during B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant predominance—eight U.S. locations, December 2020–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1167–9. 10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

