PARP1 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome
- PMID: 34529761
- PMCID: PMC8759124
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004638
PARP1 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome
Abstract
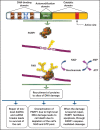
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) is a key mediator of various forms of DNA damage repair and plays an important role in the progression of several cancer types. The enzyme is activated by binding to DNA single-strand and double-strand breaks. Its contribution to chromatin remodeling makes PARP1 crucial for gene expression regulation. Inhibition of its activity with small molecules leads to the synthetic lethal effect by impeding DNA repair in the treatment of cancer cells. At first, PARP1 inhibitors (PARPis) were developed to target breast cancer mutated cancer cells. Currently, PARPis are being studied to be used in a broader variety of patients either as single agents or in combination with chemotherapy, antiangiogenic agents, ionizing radiation, and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ongoing clinical trials on olaparib, rucaparib, niraparib, veliparib, and the recent talazoparib show the advantage of these agents in overcoming PARPi resistance and underline their efficacy in targeted treatment of several hematologic malignancies. In this review, focusing on the crucial role of PARP1 in physiological and pathological effects in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia, we give an outline of the enzyme's mechanisms of action and its role in the pathophysiology and prognosis of myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia and we analyze the available data on the use of PARPis, highlighting their promising advances in clinical application.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Mego M, Cierna Z, Svetlovska D, et al. . PARP expression in germ cell tumours. J Clin Pathol. 2013;66(7):607-612. - PubMed
-
- Newman EA, Lu F, Bashllari D, Wang L, Opipari AW, Castle VP.. Alternative NHEJ pathway components are therapeutic targets in high-risk neuroblastoma. Mol Cancer Res. 2015;13(3):470-482. - PubMed
-
- Tomoda T, Kurashige T, Moriki T, Yamamoto H, Fujimoto S, Taniguchi T.. Enhanced expression of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase gene in malignant lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 1991;37(4):223-227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

