Multicentric evaluation of a novel point of care electrochemical ELISA platform for SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG and IgM antibody assay
- PMID: 34530010
- PMCID: PMC8436431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114275
Multicentric evaluation of a novel point of care electrochemical ELISA platform for SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG and IgM antibody assay
Abstract
New diagnostics technologies for the efficient detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies are very crucial to manage the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in the context of emerging vaccination paradigms. Herein, we report on a novel point-of-care Electrochemical ELISA platform with disposable screen printed electrodes functionalized with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein S1, to enable fast and accurate quantitative estimation of total antibody concentration (IgG and IgM) in clinical samples. The quantification is performed with a comparison of electrochemical redox current against the current produced by the spiked monoclonal antibodies with known concentration. The assay is validated through multicentric evaluation against 3 different FDA authorized Laboratory standard techniques, using both EDTA whole blood and serum samples. We demonstrate that the proposed assay has excellent sensitivity and specificity, making it a suitable candidate for epidemiological surveys and quantification of antibodies in COVID-19 vaccination programs.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disposable test strips; Electrochemistry; IgG/IgM antibody; Printed electrodes; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Vinay Kumar and Navakanta Bhat are the co-founders of PathShodh Healthcare Pvt. Ltd., a start-up incubated at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru. They are also the co-inventors on a US patent application 17/228,798, on this technology.
Figures
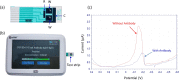


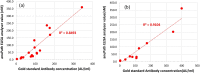
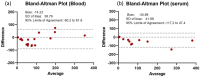
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

