Comparative study of different SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic techniques
- PMID: 34530011
- PMCID: PMC8436570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114281
Comparative study of different SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic techniques
Abstract
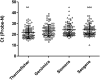
The rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 led to the necessity of developing diagnostic tests for rapid virus detection. Many commercial platforms have appeared and have been approved for this purpose. In this study, 95 positive and 5 negative retrospective samples were analyzed by 4 different commercial RT-qPCR kits (TaqMan 2019nCoV Assay, Allplex™SARS-COV-2 Assay, FTD SARS-COV-2 Assay and qCOVID-19). The Hologic Aptima SARS-COV-2 and the Clart-COVID-19 system were also tested. serial dilutions of SARS-COV-2 standard control were included for sensitivity analysis. Among the qPCR tested qCOVID19 and Allplex™SARS-COV-2 Assay were both able to detect all the clinical samples included in the study. All four qPCR evaluated showed high sensitivity for samples with Ct<33. Clart-COVID-19 microarrays detected all samples and controls used in this study whereas Hologic Aptima Panther failed with one of the clinical samples. However, the main problem with this system was the number of invalidated samples despite avoiding the use of medium with guanidine isothiocyanate as recommended by the manufacturer. All the techniques tested were of value for SARS-CoV-2 detection.
Keywords: Microarrays; RT-qPCR; SARS-CoV-2 detection; TMA.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ferreira I.C.S., Alegretti A.P., De Paris F., Paiva R.M., Chakr V.C.B.G. Comparison of a direct immunofluorescence assay (Oxoid IMAGEN®) and a multiplex RT-PCR DNA microarray assay (CLART® Pneumovir) for the detection of respiratory viruses in hospitalized children. J. Virol. Methods. 2020;284 - PubMed
-
- Kidd M., Richter A., Best A., Cumley N., Mirza J., Percival B., Mayhew M., Megram O., Ashford F., White T., Moles-García E., Crawford L., Bosworth A., Atabani S.F., Plant T., McNally A.J. S-variant SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 is associated with significantly higher viral loads in samples tested by ThermoFisher TaqPath RT-qPCR. J. Infect. Dis. 2021;13 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

