Efficacy and safety of belimumab in paediatric and adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: an across-study comparison
- PMID: 34531304
- PMCID: PMC8449964
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001747
Efficacy and safety of belimumab in paediatric and adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: an across-study comparison
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of belimumab in paediatric versus adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods: We performed across-study comparisons of patients with active SLE who received belimumab or placebo, plus standard therapy, in PLUTO (paediatric phase II) and BLISS-52, BLISS-76, BLISS-NEA and EMBRACE (adult phase III). Analysed efficacy data included Week 52 SLE Responder Index (SRI)-4 response rate (EMBRACE: SRI with modified Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) proteinuria scoring (SRI-S2K)); SRI-4 response rate (EMBRACE: SRI-S2K) according to baseline disease activity indicators (Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment-Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SELENA-SLEDAI) score; anti-dsDNA/C3/C4 levels); Week 52 SRI-6 response rate; and time to first severe flare (SELENA-SLEDAI Flare Index) over 52 weeks. Safety data were compared for all aforementioned studies along with adult LBSL02 (phase II) and BLISS-SC (phase III).
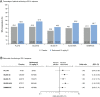
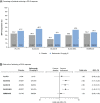
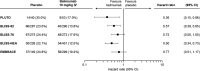
Results: SRI-4 response rates were similar across the paediatric and adult studies; more belimumab-treated patients achieved SRI-4 responses versus placebo (PLUTO: 52.8% vs 43.6%; BLISS-52: 57.6% vs 43.6%; BLISS-76: 43.2% vs 33.8%; BLISS-NEA: 53.8% vs 40.1%; EMBRACE: 48.7% vs 41.6%). Across all studies, SRI-4 response rates were generally greater in patients with baseline SELENA-SLEDAI scores ≥10 than in patients with baseline SELENA-SLEDAI scores ≤9. A similar proportion of belimumab-treated patients achieved SRI-6 across all studies (PLUTO: 41.2%; BLISS-52: 46.2%; BLISS-76: 33.1%; BLISS-NEA: 43.9%; EMBRACE: 37.5%). Belimumab reduced the risk of severe flare versus placebo in all studies. The incidence of adverse events was similar across all studies.
Conclusions: These analyses demonstrate consistent efficacy and safety of belimumab plus standard therapy across paediatric and adult patients with SLE.
Trial registration numbers: PLUTO (NCT01649765); BLISS-52 (NCT00424476); BLISS-76 (NCT00410384); BLISS-NEA (NCT01345253); EMBRACE (NCT01632241); BLISS-SC (NCT01484496); and LBSL02 (NCT00071487).
Keywords: B-lymphocytes; immune system diseases; lupus erythematosus; systemic; therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HIB has served the speakers bureau of GSK, Roche and Novartis, and has been a consultant to Hoffmann-La Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Merck Serono, AbbVie, Amgen, Alter, AstraZeneca, Baxalta Biosimilars, Biogen Idec, Boehringer, BMS, Celgene, EMD Serono, Janssen, MedImmune, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Biosciences. Payments are made to CCHMC, the employer of HIB. CA-M has received honoraria for consultancies or speaker bureaus from Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Takeda. MM has received grants from AbbVie Japan, Asahikasei Pharmaceutical, Ayumi Pharmaceutical, CSL Behring, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Japan Blood Products Organization, Nippon Kayaku and UCB Japan; lectureship fees from MSD KK; and consultancy fees from Daiichi Sankyo and Taisho Pharmaceutical. CAP, RS and DOV have no conflicts of interest to declare. ST has received grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical and Eisai; lecture fees from Eisai, Eli Lilly, Ono, Sanofi and Novartis; and consultancy fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb. RAF has received advisory board fees and travel support from GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie, AstraZeneca (MedImmune), Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Equillium, Galápagos, Genentech, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Reistone Biopharma, Sanofi, Takeda and Union Chimique Belge; and consulting fees from Alexion, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Kezar Life Sciences and MorphoS. SN has received grants from Astellas and lectureship fees from Pfizer, Novartis and Johnson & Johnson. FZ is a principal investigator at GlaxoSmithKline. DLB, GE, AEH, BNJ, MO, DAR and HQ are employees of GlaxoSmithKline and hold stocks and shares in the company. NR has received speaker's bureau and reimbursement of travel expenses from GSK, and honoraria for consultancies (<US$10 000 each) from Ablynx, AbbVie, AstraZeneca-MedImmune, Biogen, Boehringer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, GSK, Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, R-Pharma, Sanofi, Servier, Sinergie, Sobi and Takeda. The IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini (IGG), where NR works as full-time public employee, has received contributions (>US$10 000 each) from BMS, Eli Lilly, GSK, Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and Sobi. This funding has been reinvested for research activities of the hospital in a fully independent manner, without any commitment with third parties.
Figures
References
-
- Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A. Update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;2019:736–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
