Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the physiological functioning of maize under zinc-deficient soils
- PMID: 34531432
- PMCID: PMC8445980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-97742-1
Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the physiological functioning of maize under zinc-deficient soils
Abstract
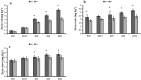
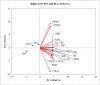
Zinc (Zn) deficiency can severely inhibit plant growth, yield, and enzymatic activities. Zn plays a vital role in various enzymatic activities in plants. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) play a crucial role in improving the plant's Zn nutrition and mitigating Zn stress effects on plants. The current study was conducted to compare the response of inoculated and non-inoculated maize (YH 1898) in the presence of different levels of zinc under greenhouse conditions under a Zn deficient condition. There were two mycorrhizal levels (i.e., M + with mycorrhizae, M- without mycorrhizae) and five Zn levels (i.e., 0, 1.5, 3, 6, and 12 mg kg-1), with three replicates following completely randomized design. At the vegetative stage (before tillering), biochemical, physiological, and agronomic attributes were measured. The results showed that maize plants previously inoculated with AMF had higher gaseous exchange traits, i.e., a higher stomatal conductance rate, favoring an increased photosynthetic rate. Improvement in antioxidant enzyme activity was also observed in inoculated compared to non-inoculated maize plants. Moreover, AMF inoculation also played a beneficial role in nutrients availability and its uptake by plants. Higher Zn12 (12 mg Zn kg-1 soil) treatment accumulated a higher Zn concentration in soil, root, and shoot in AMF-inoculated than in non-inoculated maize plants. These results are consistent with mycorrhizal symbiosis beneficial role for maize physiological functioning in Zn deficient soil conditions. Additionally, AMF inoculation mitigated the stress conditions and assisted nutrient uptake by maize.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
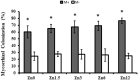
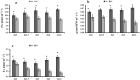
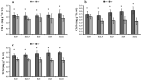
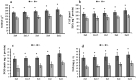
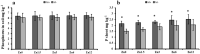
References
-
- Bibi F, et al. Effect of various application rates of phosphorus combined with different zinc rates and time of zinc application on phytic acid concentration and zinc bioavailability in wheat. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2020;54:265–272.
-
- Tahir FA, Ahamad N, Rasheed MK, Danish S. Effect of various application rate of zinc fertilizer with and without fruit waste biochar on the growth and Zn uptake in maize. Int. J. Biosci. 2018;13:159–166. doi: 10.12692/ijb/13.1.159-166. - DOI
-
- Rafique E, Rashid A, Ryan J, Bhatti AU. Zinc deficiency in rainfed wheat in Pakistan: Magnitude, spatial variability, management, and plant analysis diagnostic norms. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006;37:181–197. doi: 10.1080/00103620500403176. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

