Feeding containing the aerial part of Scutellaria baicalensis promotes the growth and nutritive value of rabbit fish Siganus fuscescens
- PMID: 34531995
- PMCID: PMC8441375
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2410
Feeding containing the aerial part of Scutellaria baicalensis promotes the growth and nutritive value of rabbit fish Siganus fuscescens
Abstract
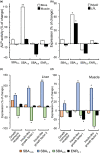
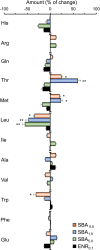
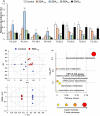
The root of Scutellaria baicalensis (Scutellaria Radix) has been used as herbal medicine for years, while its stem and leaf (aerial part) are considered as waste. The water extract from the aerial part of S. baicalensis (named as SBA) being included in the feeding of Siganus fuscescens (grey rabbit fish) has been shown to replace antibiotics in aquaculture with excellent outcome. To strengthen the usage of SBA in fish feeding, the total fish output and its nutritive value were determined here. Feeding the fishes with different doses of SBA for a month, the body length and weight were significantly increased after intake of standard feed containing 1% SBA. In parallel, the expressions of alkaline phosphatase and growth-related factors in bone, liver, and muscle of 1% SBA-fed fishes were markedly increased, suggesting the beneficial effects of SBA. The composition of amino acid and fatty acid in fish muscle, after intaking 1% SBA-containing feed, was altered. In SBA-fed fish muscle, the amounts of threonine and methionine were increased, while the amount of leucine was decreased, as compared with control group. The amounts of fatty acids, including docosahexaenoic acid, phosphatidylcholine, and phosphatidylethanolamine, were increased in the 1% SBA-fed fish, while the amounts of triglycerides were decreased. The results indicated the growth-promoting activity of SBA in an in vivo culture of S. fuscescens, as well as to increase the nutritive values of the muscle. Thus, the re-cycle of waste products during the farming of S. baicalensis herb in serving as fish feeding should be encouraged.
Keywords: Scutellaria baicalensis; feed additive; growth promotion; nutrient content analysis.
© 2021 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akazawa, N., Alvial, A., Blanc, P. P., Burgos, J., Chamberlain, G., Forster, J., Hoang, T., Ibarra, R., Khoa, L., Kibenge, F., Lightner, D., Hao, N., Nikuli, H., Omar, I., Ralaimarindaza, L., Bondad‐Reantaso, M., St‐Hilaire, S., Towner, R., Tran, L., & Villarreal, M. (2014). Reducing disease risk in aquaculture ‐ WORLD BANK REPORT NUMBER 88257‐GLB.
-
- Anh, D. J., Dimai, H. P., Hall, S. L., & Farley, J. R. (1998). Skeletal alkaline phosphatase activity is primarily released from human osteoblasts in an insoluble form, and the net release is inhibited by calcium and skeletal growth factors. Calcified Tissue International, 62(4), 332–340. 10.1007/s002239900441 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ayisi, C. L., Zhao, J., & Rupia, E. J. (2017). Growth performance, feed utilization, body and fatty acid composition of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed diets containing elevated levels of palm oil. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 2(2), 67–77. 10.1016/j.aaf.2017.02.001 - DOI
-
- Bianchi, M., Chopin, F., Farmer, T., Franz, N., Fuentevilla, C., Garibaldi, L., Grainger, N., Jara, F., Karunasagar, I., & Laurenti, A. (2014). FAO: The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
-
- Carnevali, O., Cardinali, M., Maradonna, F., Parisi, M., Olivotto, I., Polzonetti‐Magni, A. M., Mosconi, G., & Funkenstein, B. (2005). Hormonal regulation of hepatic IGF‐I and IGF‐II gene expression in the marine teleost Sparus aurata. Molecular Reproduction and Develpoment, 71(1), 12–18. 10.1002/mrd.20122 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

