Thermal stability of natural pigments produced by Monascus purpureus in submerged fermentation
- PMID: 34531997
- PMCID: PMC8441413
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2425
Thermal stability of natural pigments produced by Monascus purpureus in submerged fermentation
Abstract
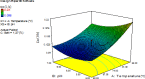
The major aim of the current study was to assess thermal stability of red pigments produced by Monascus purpureus ATCC 16362/PTCC 5303 in submerged fermentation. Natural pigments were produced by Monascus purpureus using stirred tank bioreactor. Stability of Monascus purpureus pigments was assessed under various temperature (50.2-97.8°C), salt (0%-2.5%), and pH (4.3-7.7) values. Thermal degradation constant and half-life value of the red Monascus purpureus pigments were analyzed using response surface methodology followed by a first-order kinetic reaction. Results of this study showed that pH, temperature, and salt content could affect red color stability of Monascus purpureus. The pigment showed various stabilities in various thermal conditions (temperature, salt, and pH). At high temperatures, degradation constant of the red pigments increased with decreasing pH, revealing that the Monascus red pigment was destroyed at lower pH values and salt could affect stability of the red pigments at lower temperatures.
Keywords: Monascus purpureus; natural pigments; response surface methodology; stability.
© 2021 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Aruldass, C. A., Dufossé, L., & Ahmad, W. A. (2018). Current perspective of yellowish‐orange pigments from microorganisms‐a review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 180, 168–182. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.093 - DOI
-
- Carvalho, J. C. D., Oishi, B. O., Pandey, A., & Soccol, C. R. (2005). Biopigments from Monascus: Strains selection, citrinin production and color stability. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 48(6), 885–894. 10.1590/S1516-89132005000800004 - DOI
-
- Chen, W., He, Y., Zhou, Y., Shao, Y., Feng, Y., Li, M., & Chen, F. (2015). Edible filamentous fungi from the species Monascus: Early traditional fermentations, modern molecular biology, and future genomics. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 14(5), 555–567. 10.1111/1541-4337.12145 - DOI
-
- Coultate, T., & Blackburn, R. S. (2018). Food colorants: Their past, present and future. Coloration Technology, 134(3), 165–186. 10.1111/cote.12334 - DOI
-
- Domínguez‐Espinosa, R. M., & Webb, C. (2003). Submerged fermentation in wheat substrates for production of Monascus pigments. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19(3), 329–336. 10.1023/A:1023609427750 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

