Safety assessment of HEA-enriched Cordyceps cicadae mycelia on the central nervous system (CNS), cardiovascular system, and respiratory system in ICR male mice
- PMID: 34532002
- PMCID: PMC8441276
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2440
Safety assessment of HEA-enriched Cordyceps cicadae mycelia on the central nervous system (CNS), cardiovascular system, and respiratory system in ICR male mice
Abstract
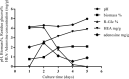
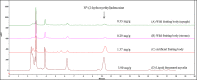
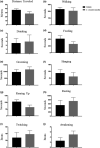
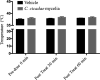
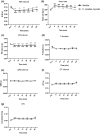
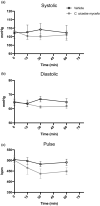
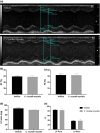
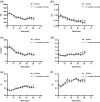
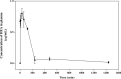
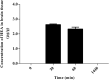
Cordyceps cicadae, an entomopathogenic fungus, is a source of traditional Chinese medicine in China. Due to the low yield of wild C. cicadae, artificial cultivation approaches will be needed to meet the increasing market demand. Using bioreactor culture can increase mass production and the abundance of the active component, N6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-adenosine (HEA). Here, we describe a safety assessment for a novel mycelium preparation method. Many studies have confirmed the safety of C. cicadae mycelia. However, the acute safety pharmacology of the C. cicadae enriched with the high HEA (3.90 mg/g) compound has not been evaluated. This study evaluated the central nervous system (CNS), cardiovascular system, and respiratory system in ICR male mice via oral gavage administration. For each requested item, two batches of eight mice tested on a vehicle (0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose, CMC) and C. cicadae mycelia (1,000 mg/kg) were performed. The heart rate at 60 min for the vehicle and C. cicadae mycelium treatment was 700.3 ± 55.4 and 603.0 ± 42.3 bpm, respectively (p = .4279). For echocardiographic analysis, the LV mass of the vehicle and drug treatment was 86.7 ± 6.4 and 80.2 ± 7.7, respectively (p = .0933). In the respiratory test, the tidal volume of the vehicle and drug treatments was 0.11 ± 0.01 and 0.14 ± 0.01 at 60 min, respectively (p = .4262). These results demonstrate that the oral administration of HEA-enriched C. cicadae mycelia is safe for the CNS, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems.
Keywords: Cordyceps cicadae mycelia; Liquid fermentation; N6‐(2‐hydroxyethyl) adenosine; safety assessment.
© 2021 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham, J. (2010). International Conference On Harmonisation Of Technical Requirements For Registration Of Pharmaceuticals For Human Use. In Tietje C., & Brouder A. (Eds), Handbook of Transnational Economic Governance Regimes (4th ed.,pp. 1041–1053). Brill, Nijhoff. 10.1163/ej.9789004163300.i-1081.897 - DOI
-
- Chen, Y. L., Yeh, S. H., Lin, T. W., Chen, C. C., Chen, C. S., & Kuo, C. F. (2015). A 90‐Day Subchronic Toxicity Study of Submerged Mycelial Culture of Cordyceps cicadae (Ascomycetes) in Rats. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 17(8), 771–781. 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.v17.i8.70 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deng, J. S., Jiang, W. P., Chen, C. C., Lee, L. Y., Li, P. Y., Huang, W. C., Liao, J. C., Chen, H. Y., Huang, S. S., & Huang, G. J. (2020). Cordyceps cicadae Mycelia Ameliorate Cisplatin‐Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Suppressing the TLR4/NF‐ κ B/MAPK and Activating the HO‐1/Nrf2 and Sirt‐1/AMPK Pathways in Mice. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2020, 1–17. 10.1155/2020/7912763 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

