Detection of Cell Death in Planarians
- PMID: 34532516
- PMCID: PMC8342080
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3039
Detection of Cell Death in Planarians
Abstract
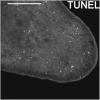
Planarians are freshwater flatworms, well known for their ability to regenerate a complete organism from any piece of their body. Furthermore, planarians are constantly growing and degrowing throughout their lives, maintaining a functional and proportioned body. These properties rely on the presence of a population of adult stem cells and on the tight control of their cell renewal, which is based on the balance between the proliferation of new cells and their differentiation, and the death of unnecessary cells. Due to the importance of these two processes in planarian biology, over the years, researchers have optimized molecular techniques to detect both cell proliferation and cell death in planarians. Here, we present the two main protocols currently used for cell death detection and quantification in the planarian field: Caspase-3 activity quantification and TUNEL assay.
Keywords: Caspase-3 activity; Cell death; Cell turnover; Planarians; TUNEL assay.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no conflicts of interest or competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Baguñá J. and Romero R.(1981). Quantitative analysis of cell types during growth, degrowth and regeneration in the planarians Dugesia mediterranea and Dugesia tigrina . Hydrobiologia 84: 181-194.
-
- de Sousa N.(2017). Ph.D. Thesis. Role of Hippo pathway in planarians. University of Barcelona.
-
- González-Estévez C. and Salo E.(2010). Autophagy and apoptosis in planarians. Apoptosis 15(3): 279-292. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

