Machine learning to investigate superficial white matter integrity in early multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 34532924
- PMCID: PMC8752496
- DOI: 10.1111/jon.12934
Machine learning to investigate superficial white matter integrity in early multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background and purpose: This study aims todetermine the sensitivity of superficial white matter (SWM) integrity as a metric to distinguish early multiple sclerosis (MS) patients from healthy controls (HC).
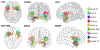
Methods: Fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity (MD) values from SWM bundles across the cortex and major deep white matter (DWM) tracts were extracted from 29 early MS patients and 31 age- and sex-matched HC. Thickness of 68 cortical regions and resting-state functional-connectivity (RSFC) among them were calculated. The distribution of structural and functional metrics between groups were compared using Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Utilizing a machine learning method (adaptive boosting), 6 models were built based on: 1-SWM, 2-DWM, 3-SWM and DWM, 4-cortical thickness, or 5-RSFC measures. In model 6, all features from previous models were incorporated. The models were trained with nested 5-folds cross-validation. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUCroc ) values were calculated to evaluate classification performance of each model. Permutation tests were used to compare the AUCroc values.
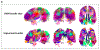
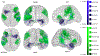
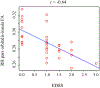
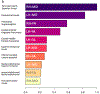
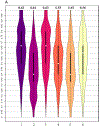
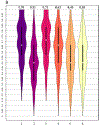
Results: Patients had higher MD in SWM bundles including insula, inferior frontal, orbitofrontal, superior and medial temporal, and pre- and post-central cortices (p < .05). No group differences were found for any other MRI metric. The model incorporating SWM and DWM features provided the best classification (AUCroc = 0.75). The SWM model provided higher AUCroc (0.74), compared to DWM (0.63), cortical thickness (0.67), RSFC (0.63), and all-features (0.68) models (p < .001 for all).
Conclusion: Our results reveal a non-random pattern of SWM abnormalities at early stages of MS even before pronounced structural and functional alterations emerge.
Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging; machine learning; multiple sclerosis; superficial white matter; u-fibers.
© 2021 American Society of Neuroimaging.
Figures



References
-
- Bae HG, Kim TK, Suk HY, et al. White matter and neurological disorders. Arch Pharm Res 2020;43:920–31. - PubMed
-
- Wycoco V, Shroff M, Sudhakar S, et al. White matter anatomy: what the radiologist needs to know. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2013;23:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Ciccarelli O, Barkhof F, Bodini B, et al. Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: insights from molecular and metabolic imaging. Lancet Neurol 2014;13:807–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

