[Review of clinical practice guidelines for hypoparathyroidism]
- PMID: 34533015
- PMCID: PMC9753818
- DOI: 10.14341/probl12800
[Review of clinical practice guidelines for hypoparathyroidism]
Abstract
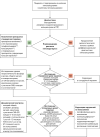
Hypoparathyroidism is a rare disorder characterized by the absent or inappropriately decreased serum parathyroid hormone in the parathyroid glands, which is accompanied by impaired calcium-phosphorus metabolism.The main etiology of hypoparathyroidism remains damage or removal of the parathyroid glands during neck surgery. In view of the incidence of thyroid cancer, primary hyperparathyroidism and other pathologies of the neck organs, which radical treatment can lead to the parathyroid gland impairment, an increased number of patients with hypoparathyroidism is expected. Autoimmune hypoparathyroidism is the second most common form of the disease, usually occurring as part of type 1 autoimmune polyglandular syndrome. Autoimmune hypoparathyroidism usually occurs in childhood and is characterized by a severe course of the disease, especially in the case of concomitant malabsorption syndrome.Chronic hypoparathyroidism of any etiology requires lifelong multicomponent therapy, as well as careful monitoring and an individual approach to choose the optimal treatment strategy. In the absence of adequate follow-up, the risks of long-term complications significantly increase, particularly in the renal, cardiovascular systems; in the soft tissues and in the brain, it could lead to visual disturbances; pathology of the musculoskeletal system with a decreased bone remodeling and a potential risk of fractures, as well as to the neurocognitive disorders and an impaired health-related quality of life.Timely diagnosis, rational medical therapy and management strategy may reduce the risks of short-term and long-term complications, frequency of hospitalizations and disability of patients, as well as improve the prognosis.This review covers the main issues of Russian guidelines for the management of chronic hypoparathyroidism, approved in 2021, including laboratory and instrumental evaluation, treatment approaches and follow-up. This guidelines also include the recommendations for special groups of patients: with acute hypocalcemia, hypoparathyroidism during pregnancy.
Гипопаратиреоз — эндокринное заболевание, характеризующееся сниженной продукцией паратиреоидного гормона околощитовидными железами или резистентностью тканей к его действию, что сопровождается нарушениями фосфорно-кальциевого обмена.Основной этиологией гипопаратиреоза является повреждение или удаление околощитовидных желез во время хирургического вмешательства на органах шеи. Ввиду распространенности рака щитовидной железы, первичного гиперпаратиреоза и других патологий органов шеи, радикальное лечение которых может привести к развитию гипопаратиреоза, прогнозируется неуклонный рост и увеличение числа больных с этой патологией. Аутоиммунный гипопаратиреоз — вторая по распространенности форма заболевания, встречающаяся, как правило, в рамках аутоиммунного полигландулярного синдрома 1 типа. Гипопаратиреоз в рамках этого синдрома возникает в детском возрасте и, как правило, характеризуется более тяжелым течением, особенно в случае сопутствующего синдрома мальабсорбции.Развитие хронического гипопаратиреоза любой этиологии требует пожизненного назначения многокомпонентной терапии, а также тщательного мониторинга и индивидуального подхода к ведению заболевания. В отсутствие адекватного динамического наблюдения развиваются множественные осложнения со стороны жизненно важных органов, в частности кальцификация мочевыделительной системы (нефрокальциноз, нефролитиаз с развитием почечной недостаточности), мягких тканей и головного мозга; сердечно-сосудистые нарушения; зрительные расстройства; патология костно-мышечной системы со снижением костного ремоделирования и потенциальным риском переломов, а также развитием нейрокогнитивных расстройств и резким снижением качества жизни пациентов.Своевременная диагностика, рационально подобранная лекарственная терапия и грамотное ведение пациента позволят снизить риски развития осложнений, позволят улучшить прогноз, снизить частоту госпитализаций и инвалидизаций пациентов с данным заболеванием.В статье изложены основные тезисы клинических рекомендаций по ведению пациентов с гипопаратиреозом, утвержденных Минздравом России в 2021 г. Изложены алгоритмы диагностики, лечения и динамического наблюдения за пациентами с данной нозологией. Отдельные разделы посвящены купированию острой гипокальциемии, а также ведению беременности у пациенток с гипопаратиреозом.
Figures
References
-
- Butters Robert R., Chattopadhyay Naibedya, Nielsen Palle, Smith Craig P., Mithal Ambrish, Kifor Olga, Bai Mei, Quinn Steven, Goldsmith Paul, Hurwitz Shmuel, Krapcho Karen, Busby James, Brown Edward M.. Cloning and Characterization of a Calcium-Sensing Receptor from the Hypercalcemic New Zealand White Rabbit Reveals Unaltered Responsiveness to Extracellular Calcium. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2006 Apr;12(4):568–579. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1997.12.4.568. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources