Application of artificial intelligence to the electrocardiogram
- PMID: 34534279
- PMCID: PMC8500024
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab649
Application of artificial intelligence to the electrocardiogram
Abstract
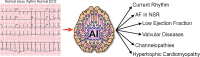
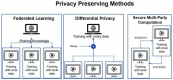
Artificial intelligence (AI) has given the electrocardiogram (ECG) and clinicians reading them super-human diagnostic abilities. Trained without hard-coded rules by finding often subclinical patterns in huge datasets, AI transforms the ECG, a ubiquitous, non-invasive cardiac test that is integrated into practice workflows, into a screening tool and predictor of cardiac and non-cardiac diseases, often in asymptomatic individuals. This review describes the mathematical background behind supervised AI algorithms, and discusses selected AI ECG cardiac screening algorithms including those for the detection of left ventricular dysfunction, episodic atrial fibrillation from a tracing recorded during normal sinus rhythm, and other structural and valvular diseases. The ability to learn from big data sets, without the need to understand the biological mechanism, has created opportunities for detecting non-cardiac diseases as COVID-19 and introduced challenges with regards to data privacy. Like all medical tests, the AI ECG must be carefully vetted and validated in real-world clinical environments. Finally, with mobile form factors that allow acquisition of medical-grade ECGs from smartphones and wearables, the use of AI may enable massive scalability to democratize healthcare.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Digital health; Electrocardiograms; Machine learning.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2021. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Attia ZI, Kapa S, Lopez-Jimenez F, McKie PM, Ladewig DJ, Satam G, Pellikka PA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Noseworthy PA, Munger TM, Asirvatham SJ, Scott CG, Carter RE, Friedman PA. Screening for cardiac contractile dysfunction using an artificial intelligence-enabled electrocardiogram. Nat Med 2019;25:70–74. - PubMed
-
- Attia ZI, Noseworthy PA, Lopez-Jimenez F, Asirvatham SJ, Deshmukh AJ, Gersh BJ, Carter RE, Yao X, Rabinstein AA, Erickson BJ, Kapa S, Friedman PA. An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for the identification of patients with atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm: a retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. Lancet 2019;394:861–867. - PubMed
-
- Selvaraju RR, Cm Das A, Vedantam R, Parikh D, Batra D. Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis (ICCV) 2017;618–626.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

