Cancer and diabetes: the interlinking metabolic pathways and repurposing actions of antidiabetic drugs
- PMID: 34535145
- PMCID: PMC8447515
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-02202-5
Cancer and diabetes: the interlinking metabolic pathways and repurposing actions of antidiabetic drugs
Abstract
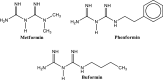
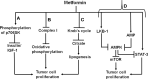
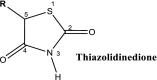
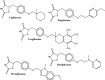
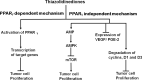
Cancers are regarded as one of the main causes of death and result in high health burden worldwide. The management of cancer include chemotherapy, surgery and radiotherapy. The chemotherapy, which involves the use of chemical agents with cytotoxic actions is utilised as a single treatment or combined treatment. However, these managements of cancer such as chemotherapy poses some setbacks such as cytotoxicity on normal cells and the problem of anticancer drug resistance. Therefore, the use of other therapeutic agents such as antidiabetic drugs is one of the alternative interventions used in addressing some of the limitations in the use of anticancer agents. Antidiabetic drugs such as sulfonylureas, biguanides and thiazolidinediones showed beneficial and repurposing actions in the management of cancer, thus, the activities of these drugs against cancer is attributed to some of the metabolic links between the two disorders and these includes hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinemia, inflammation, and oxidative stress as well as obesity. Furthermore, some studies showed that the use of antidiabetic drugs could serve as risk factors for the development of cancerous cells particularly pancreatic cancer. However, the beneficial role of these chemical agents overweighs their detrimental actions in cancer management. Hence, the present review indicates the metabolic links between cancer and diabetes and the mechanistic actions of antidiabetic drugs in the management of cancers.
Keywords: Anticancer drugs; Antidiabetic drugs; Cancer; Diabetes; Repurposing action.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No Competing Interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nejati-Koshki K, Zarghami N, Pourhassan-Moghaddam M, Rahmati-Yamchi M, Mollazade M, Nasiri M, Esfahlan RJ, Barkhordari A, Tayefi-Nasrabadi H. Inhibition of leptin gene expression and secretion by silibinin: possible role of estrogen receptors. Cytotechnology. 2012;64(6):719–726. doi: 10.1007/s10616-012-9452-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

